Introduction
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, optimizing production efficiency is crucial for maximizing output and profitability. Traditional methods of monitoring machine health often fall short, leading to missed opportunities for improvement.
This Article aims to introduce the key features of an NCD Dashboard. This dashboard allows visualization of data from the Machine Uptime Monitoring Sensor, an innovative solution designed to track and analyze the operational efficiency of industrial machinery in real-time. Additionally, it will provide instructions on how to import this subflow into your Node-RED project. Ultimately, this solution offers a visual tool that simplifies working with the sensor in an easy and intuitive way.
Machine Uptime Monitoring Sensor
A groundbreaking innovation designed to streamline machine and production uptime tracking within industrial environments. The Machine Uptime Monitoring Sensor leverages cutting-edge technology, including accelerometers, magnetometers, digital input, and current sensor readings. This powerful device delivers real-time monitoring capabilities with unparalleled accuracy.
These innovative sensors offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for capturing critical Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as machine availability, cycle durations, and operational time. By continuously tracking these metrics, you gain valuable insights into the health and performance of your machinery.
Benefits of Machine Uptime Monitoring:
- Enhanced Production Efficiency: By identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, you can make data-driven decisions to optimize your production processes.
- Reduced Downtime: Real-time monitoring allows for proactive maintenance, minimizing unplanned downtime and ensuring smooth operation.
- Improved Decision Making: Access to accurate production data empowers you to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, capacity planning, and overall production strategy.
You want to learn How to calculte Machine Utilization using IoT visit this Article. Or learn how to integrate the NCD Machine Uptime Sensor with Datacake, Qubitro and Tago IO:
Overview
The next image is a visual representation of this Article. The sensor(s) collect the data of interest from the field elements, and then send the signal via Digi-Mesh to the Enterprise IIoT Gateway or Industrial IoT Wireless Modem, where it is processed by Node-RED and then sent to the NCD-Dashboard for storage and intuitive visualization.
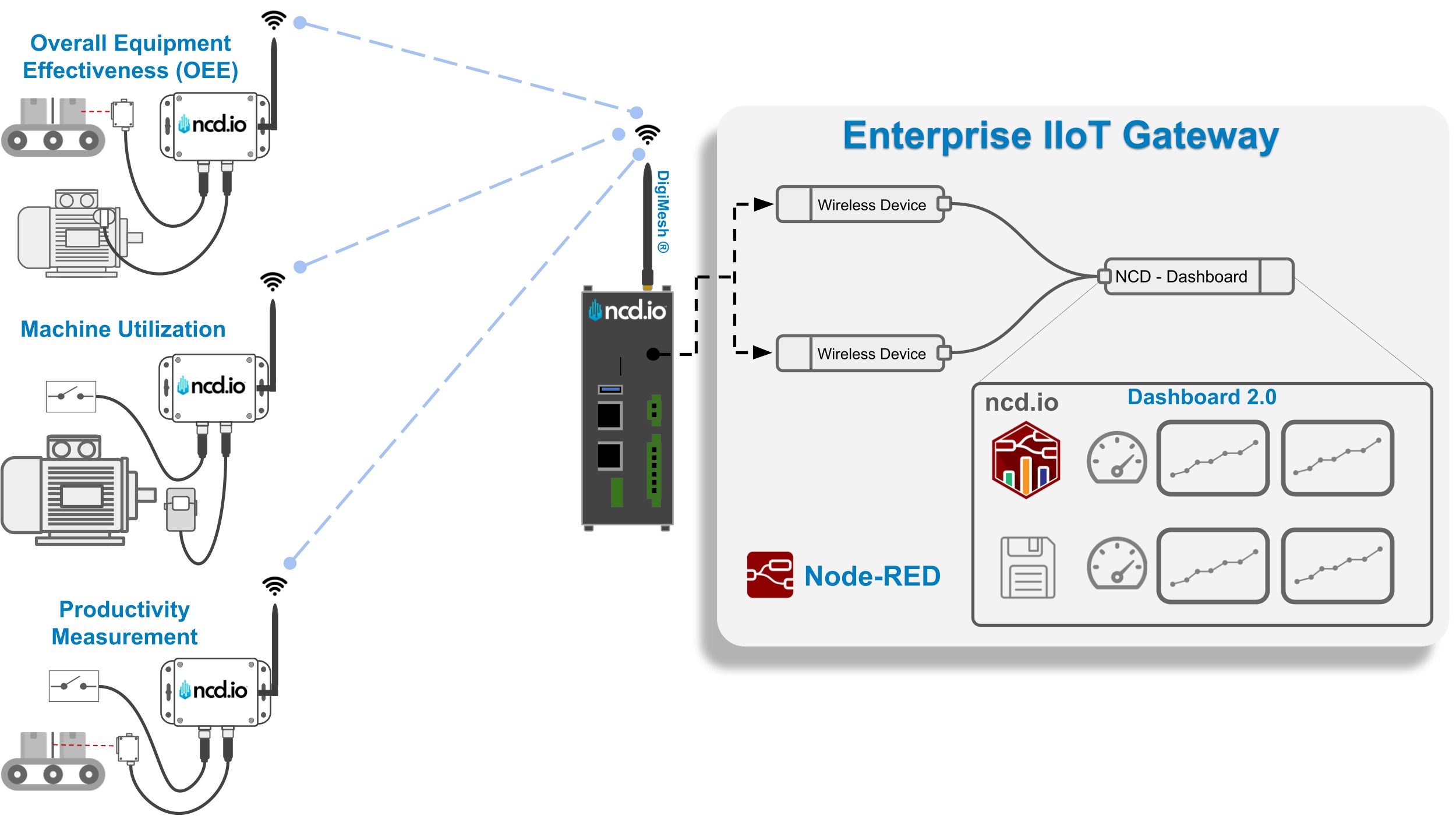
Highlights
Real-Time Data
Real-time display of the variables emitted by the sensor:
- Contact Closure
- Current Sensor
- Digital Input
- Accelerometer Sensor
- Magnetometer Sensor
Historical Data
Historical data visualization of the values of the variables emitted by the sensor.
Detection by Type
Machine Uptime Monitoring Sensor.
Data Inspection
Function to inspect from the dashboard the object data coming from the sensor(s).
Dynamic Sensor Selection via MAC Address
- Dynamic Data Loading: This feature allows your NCD Dashboard to automatically update the displayed information based on user selection.
- Sensor Selection via MAC Address: Users can choose the sensor they want to see data from using a dropdown menu that lists sensors by their unique MAC address.
- Automatic Data Update: Once a sensor is selected, the NCD Dashboard automatically retrieves and displays the relevant data for that specific sensor.
Datalogger
Generation and storage in local (or user-defined) path of CSV file with data from the sensor(s).
On-Demand Download
- Convenient Data Export: Download sensor data as CSV files directly from your web browser.
- Local File Access Not Required: Download the CSV file to any device within your local network, regardless of where the dashboard is hosted.
Requirements
Before you begin using the NCD-Dashboard, you’ll need to have the following software installed:
- Node-RED
- NCD Library
- FlowFuse Dashboard 2
Note: An Internet connection is required on your PC or Enterprise IIoT Gateway during the installation process.
Node-RED
Node-RED, is a visual programming tool, It provides a browser-based editor that allows creating applications by wiring predefined black box functions (nodes) . Despite its technical nature, Node-RED offers a user-friendly interface.
Node-RED is an open-source project under the OpenJS Foundation. This means it’s free to use, without any monthly subscription fees. You can install and run Node-RED locally on your PC, Raspberry Pi, or, in the case of our Enterprise IIoT Gateway, it comes pre-installed and runs as a service.
Key Features:
Open Source: Node-RED is freely available for use and modification, making it a cost-effective and transparent choice.
Local Installation: Run Node-RED directly on your device, providing complete control over data and privacy.
Pre-installed on Enterprise IIoT Gateway and Enterprise IIoT Gateway Lite: For seamless integration and simplified deployment in IIoT environments.
Sensor Data Processing and Delivery Flexibility
Every NCD sensor packet creates a message (object) that flows through connected nodes within Node-RED. These nodes allow you to:
- Modify the message to suit your specific application needs.
- Package the data into various protocols like MQTT, Modbus, or OPC-UA.
Send the data directly to your preferred cloud platform (Azure, AWS, Ubidots, Losant, etc.). - Inject the data directly into an SQL or NoSQL database.
- Integrate with SCADA systems like Ignition SCADA.
Here you can find a complete getting started guide for accessing Node-RED from the Enterprise IIoT Gateway:
Note: To perform the installation process of Node-RED on Windows operating system, you can follow the steps in this article:
NCD Enterprise Sensor Library for Node-RED
This library handles communication to, and configuration of, the NCD Wireless Sensor Line. It can be used in conjunction with Node-RED to create and manage a Wireless Sensor Network using the Node-RED flow-based development tool on any platform.
Step 1. Within your Node-RED instance go to the main menu (top right) and select the “Manage palette” option:
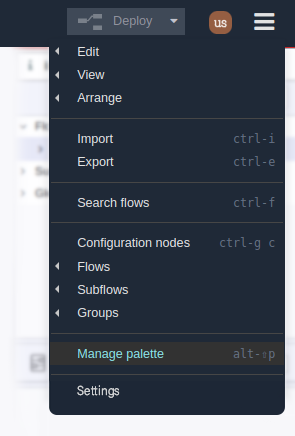
Step 2.- The “User Settings” window will be displayed, inside “Palette” you must select click on the “Install” tab.
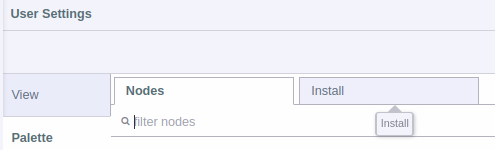
Step 3.- In Search Field enter “@ncd-io/node-red-enterprise-sensors”, you will see the following:
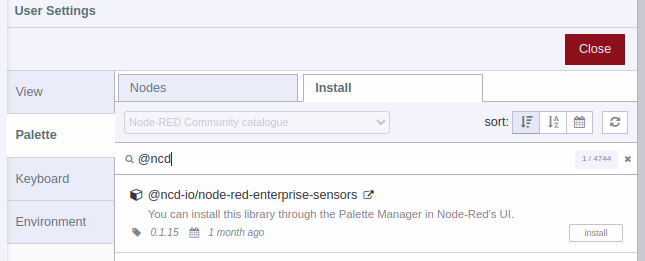
Step 4.- Click the “Install” button to start the installation process, a window will appear at the top of the screen, asking you to confirm the installation:
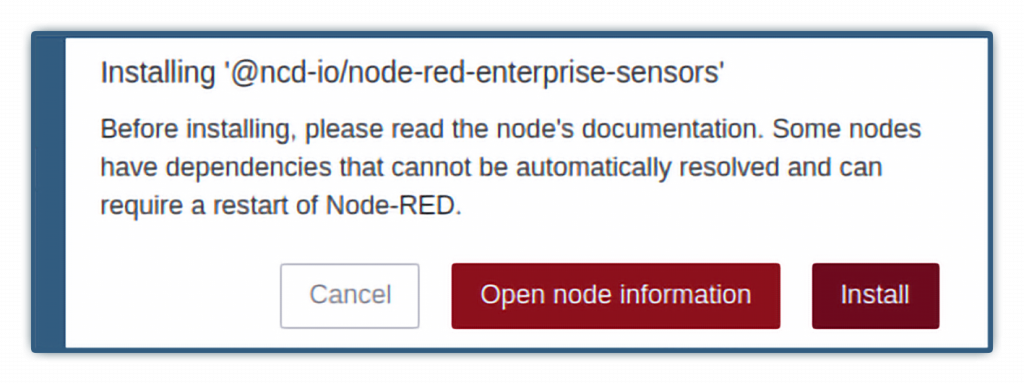
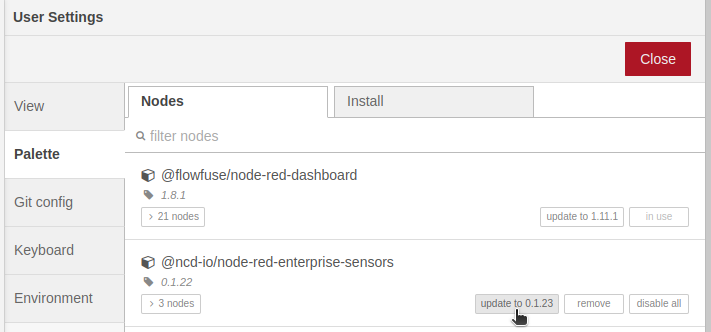
Step 5.- Once the process is completed you will see the following window:

See the following GIF for a visual demonstration of the installation process:

Note: you can find the Enterprise Sensor Library Documentation here:
https://flows.nodered.org/node/@ncd-io/node-red-enterprise-sensors
FlowFuse Dashboard 2.0

FlowFuse Dashboard 2.0 is an easy to use collection of nodes for Node-RED that allows you to create data-driven Dashboards & data visualizations. Installation procedure is similar to the previous one, FlowFuse’s Node-RED Dashboard 2.0 is also available in the Node-RED Palette Manager.
Source: https://dashboard.flowfuse.com/
Installation procedure:
Step 1.- Open the menu in the top-right of Node-RED, then Click “Manage Palette”:

Step 2.- Switch to the “Install” tab, Search “@flowfuse/node-red-dashboard”, Install the package:
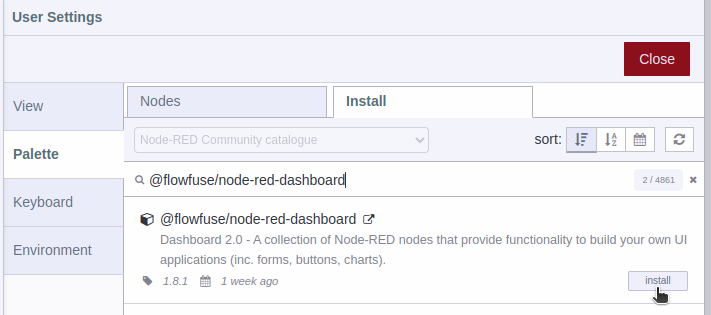
Step 3.- You must confirm the installation by clicking on the Install button in the pop-up window.
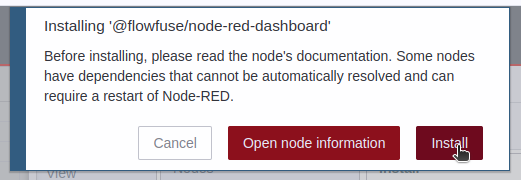
Step 4.- You will see a list of the dashboard 2 nodes that have been installed.

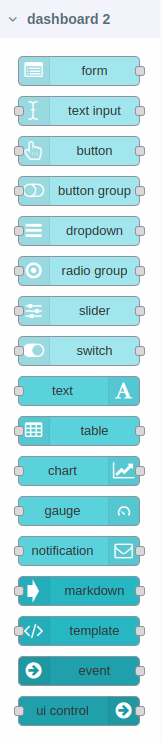
Step 5.- In workspace you can see the available nodes in the nodes palette, as shown in the following image:
The following GIF for a visual demonstration of the installation process:

Importing NCD Dashboard
After successfully installing Node-RED and Dashboard 2.0, you’re ready to import the NCD Dashboard, which is specifically designed and optimized for NCD sensors. The process is straightforward, but be sure to follow these steps carefully:
- Copy the JSON: Locate the NCD Dashboard JSON file.
- Import the JSON: Within Node-RED, use the import function to bring in the copied JSON file.
This will import the NCD Dashboard elements into your Node-RED workspace, allowing you to visualize and interact with your NCD sensor data.
Step 1 - Copy JSON
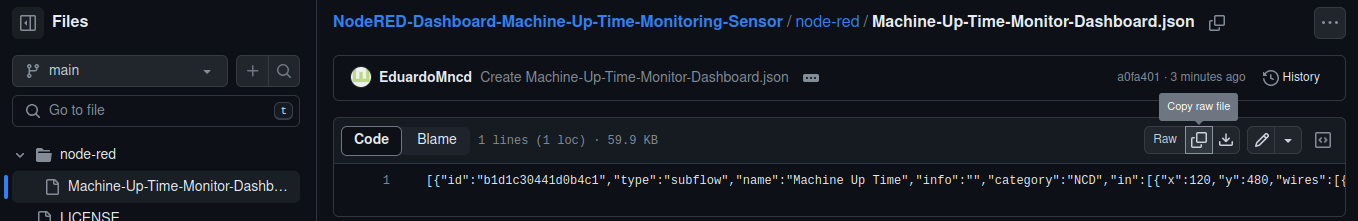
1. Copy the raw JSON file “node-red/Machine-Up-Time-Monitor-Dashboard.json” from this repository:
2. Once the repository is open, locate the button that allows you to copy the raw JSON code of the dashboard. Refer to the following image for a visual reference:
Step 2 - Import the JSON
With the NCD Dashboard source code copied, head back to the Node-RED node editor and follow these next steps carefully:
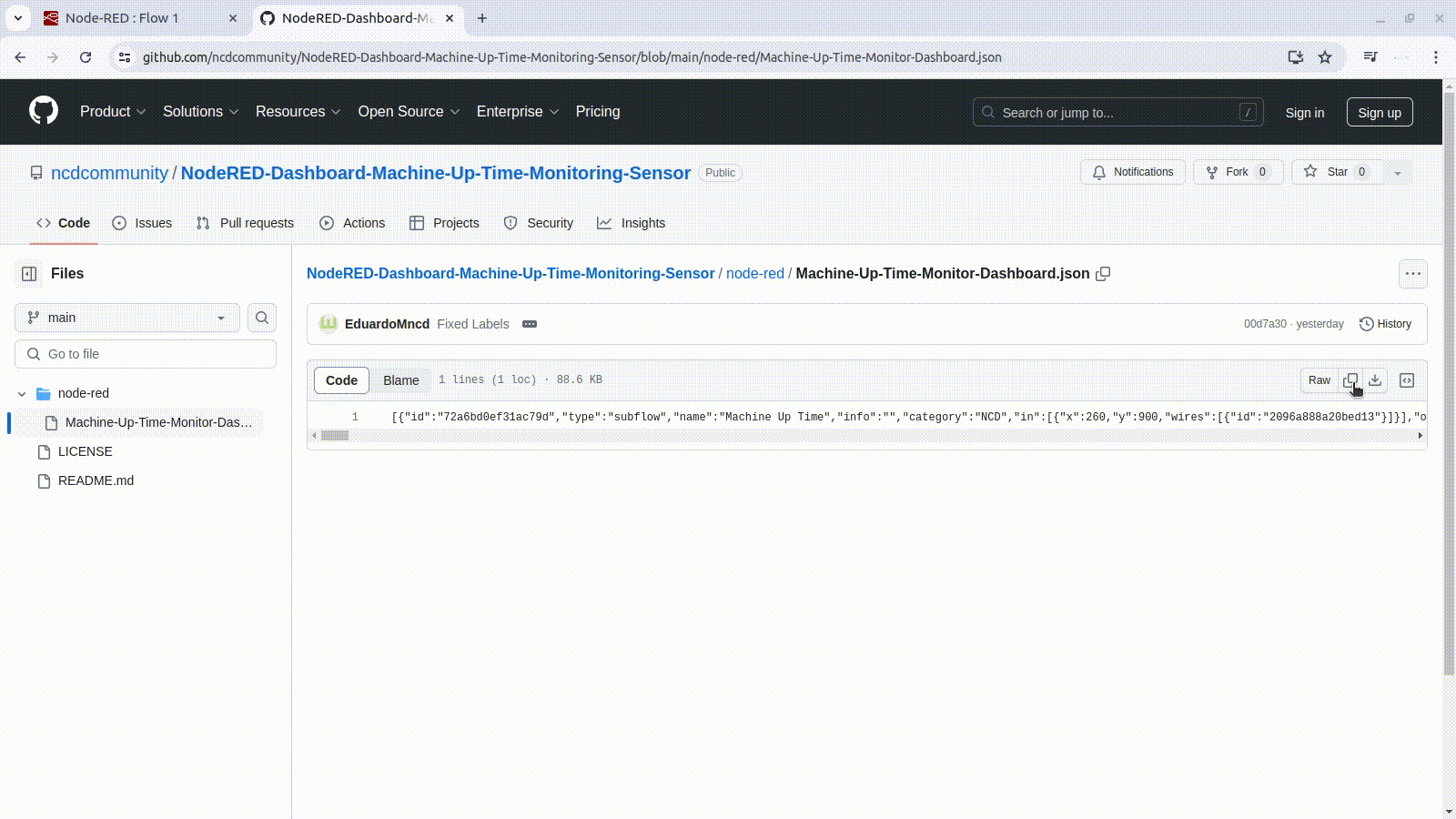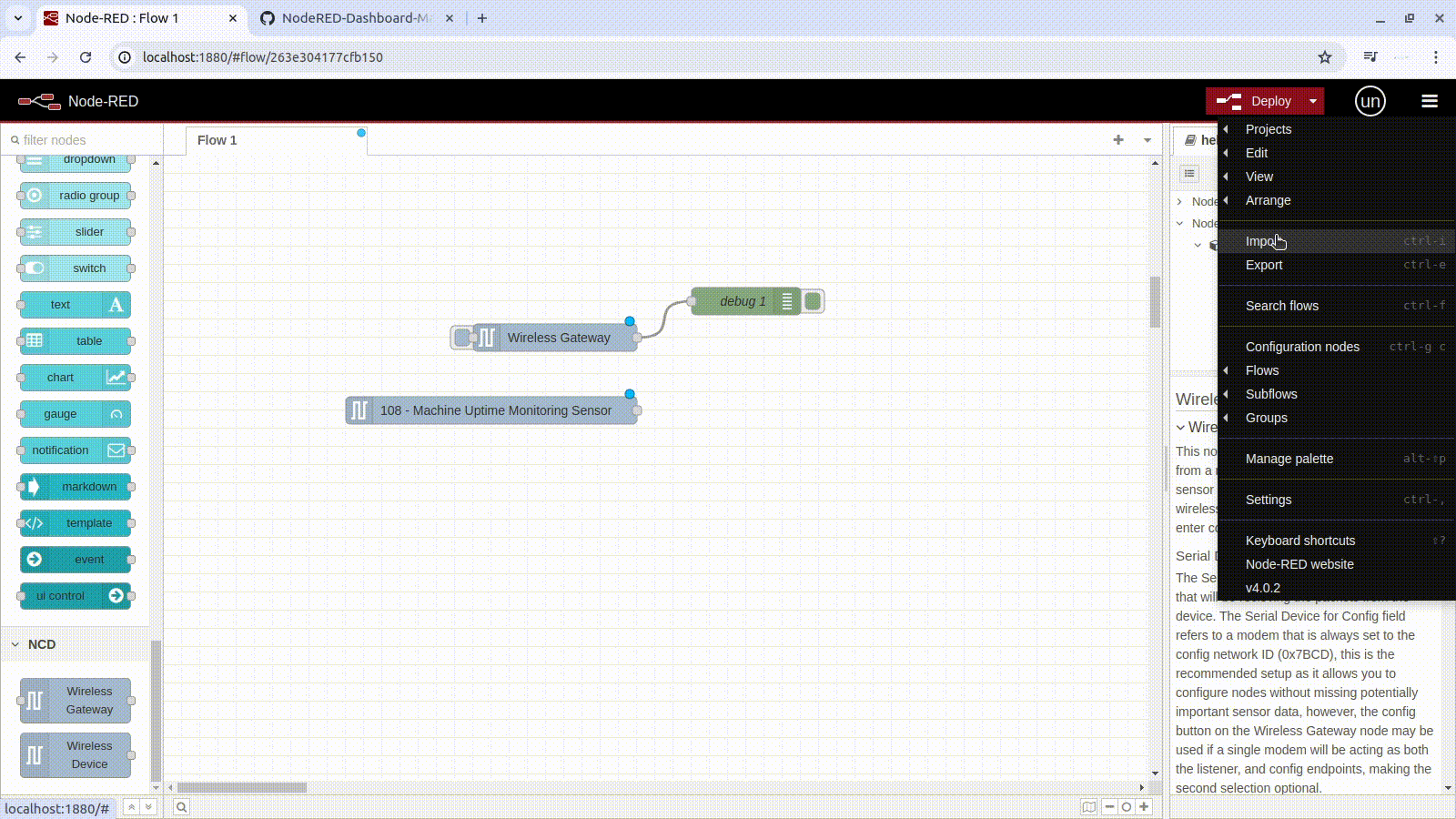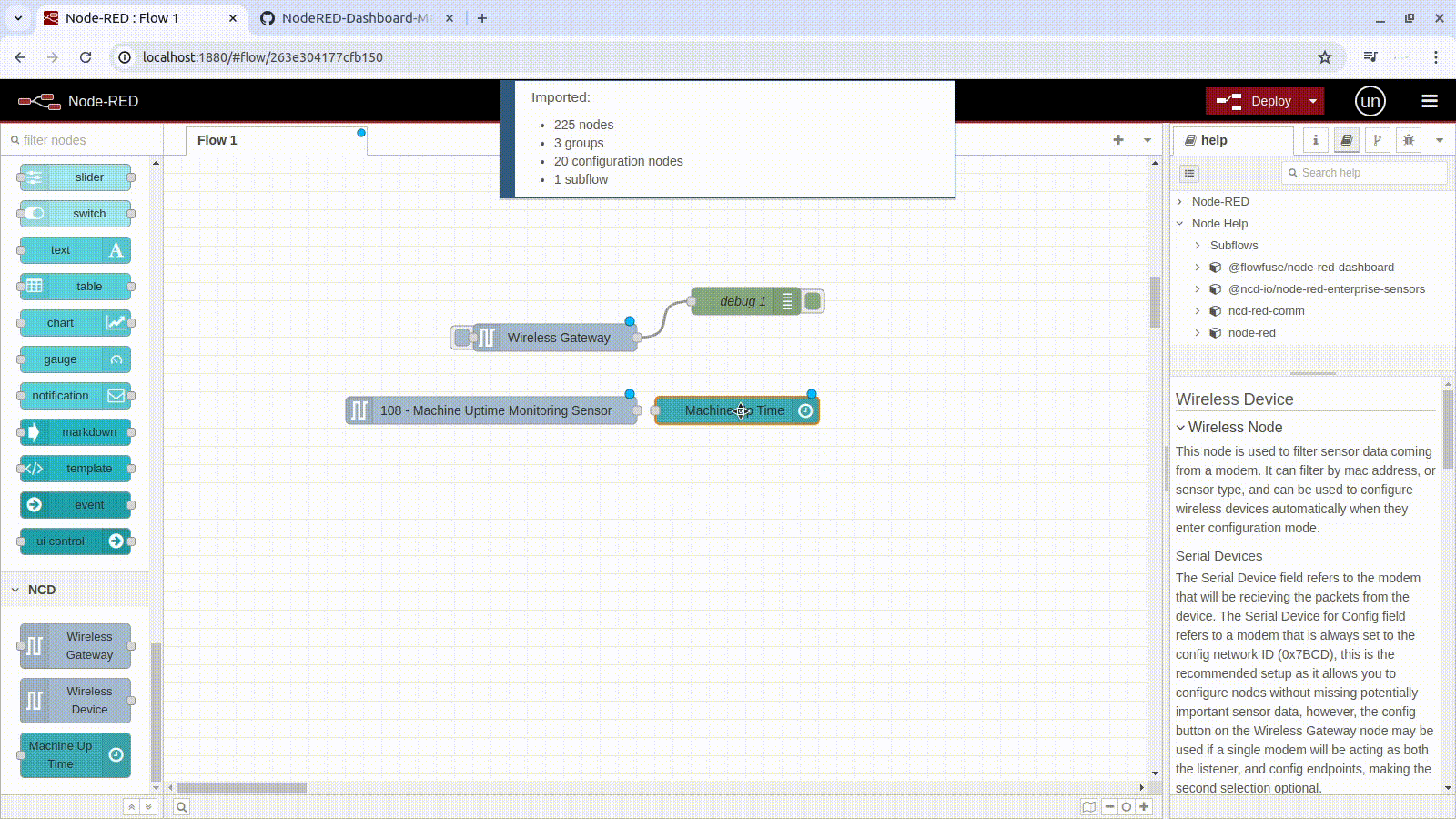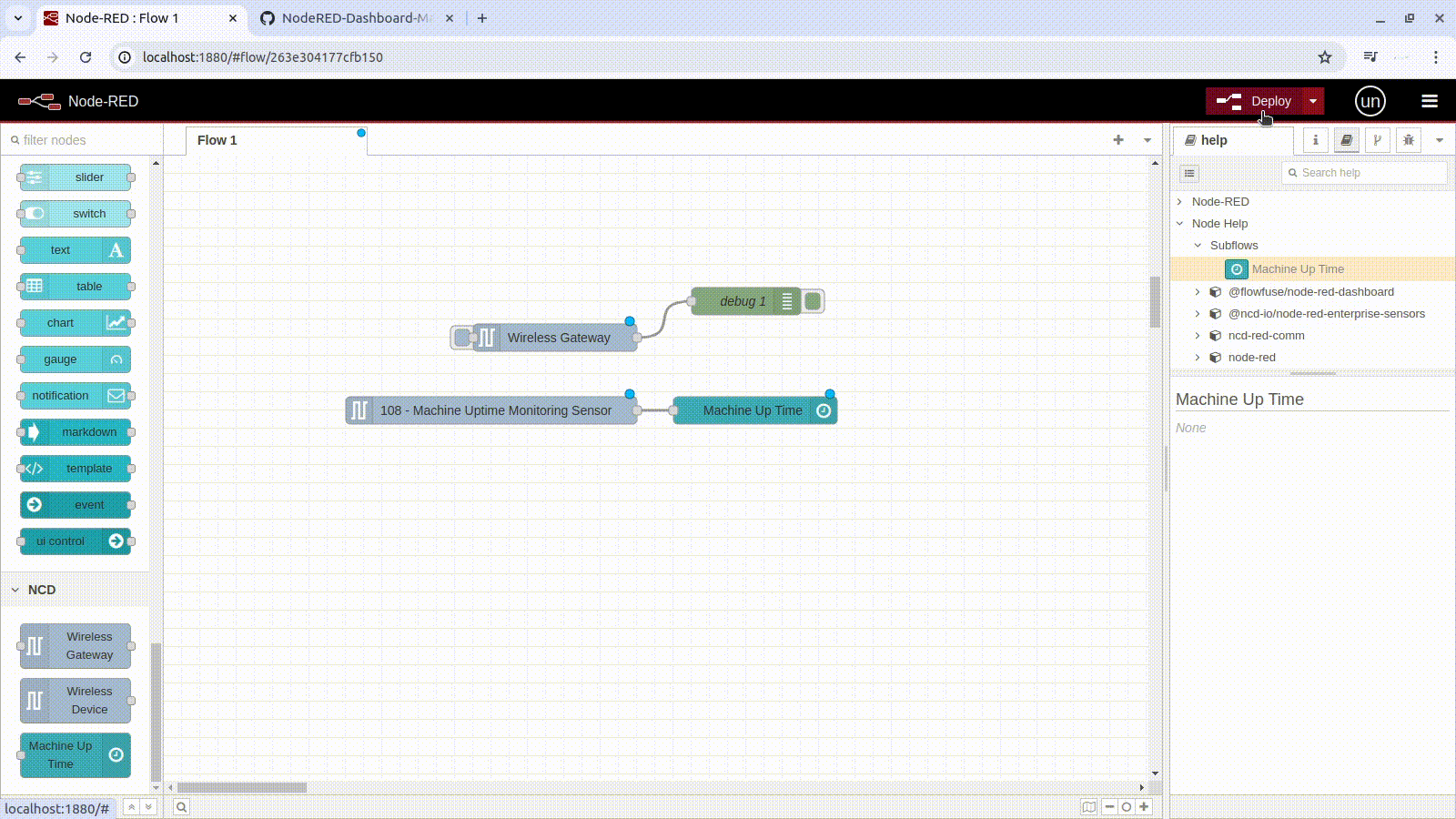
1.- Go to the Main Menu (hamburger icon in the upper right corner) then click on “Import” option, as shown in picture.
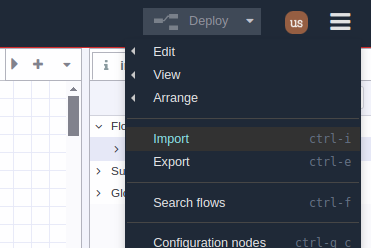
2.- A text-box will be opened. Right click and paste the JSON code you just copied from GitHub, as shown in picture:
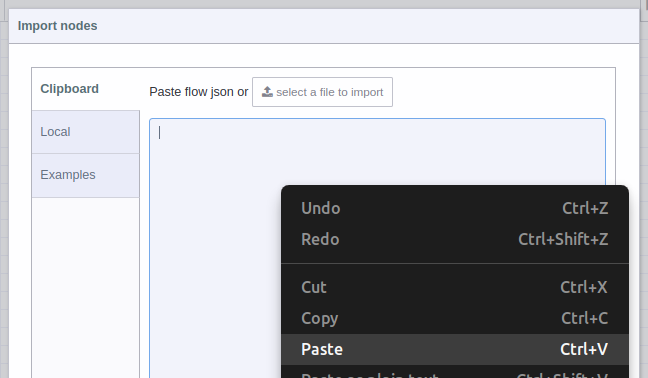
3.- You should see the JSON code in text-box, now you can press the red “Import” button at the bottom right (by default the “current flow” option is selected):
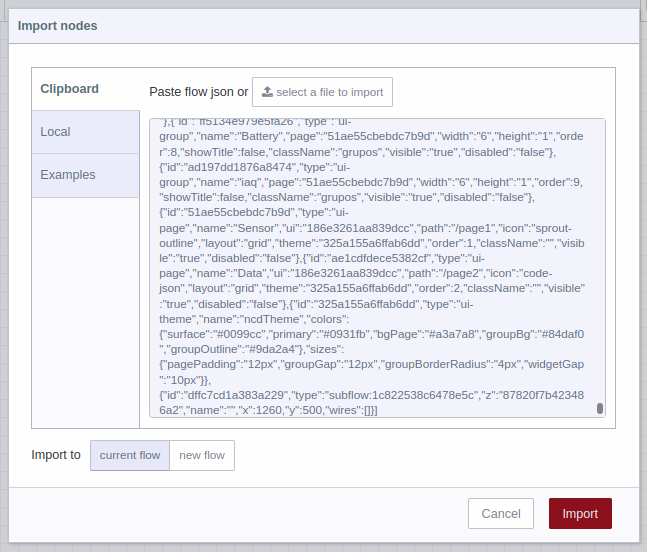
4.- In the top of the Node-RED editor, you will see information of the NCD-Dashboard you just imported, and automatically you will have the node available inside the node editor, now you can position it inside the editor or workspace by left clicking:
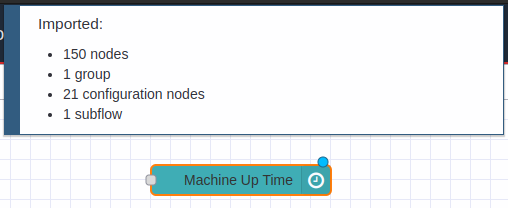
5.- You may also notice that the NCD-Dashboard node has been added to the NCD node group in nodes palette.
This GIF provides a visual demonstration of the importing process.
Configuring
This section delves into configuring and connecting nodes within the Node-RED editor. Here, we’ll explore:
- Configure NCD Nodes: how to set up NCD Nodes to get data from sensors.
- Node Connections: Learn how to establish connections between your nodes to create the desired data flow.
- Properties and Data Storage Configuration: Discover the property that allows you to define the path where sensor data will be stored within the NCD-Dashboard node.
- NCD Dashboard Node Status: Understand how to utilize the visual node status feature to monitor the operational state of each node.
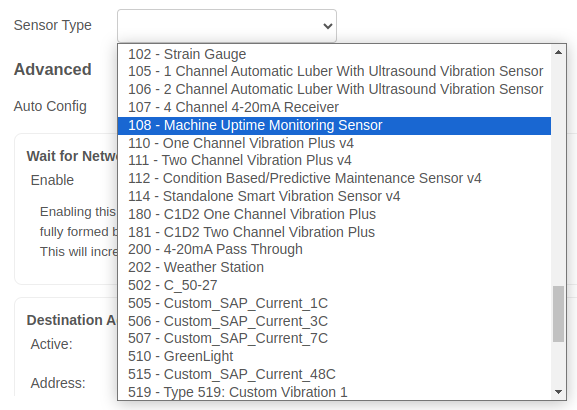
1 - Configure NCD Nodes
The first step is to configure your ncd nodes (you may have already configured your nodes), but it is important to remember that this NCD-Dashboard only works for “Machine Up Time Monitorig” type:
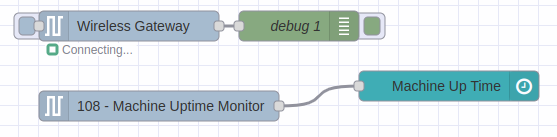
2. Node Connections
With your NCD nodes configured and sensor data flowing, the next step is to connect the output of the “NCD Wireless Device” node (corresponding to the sensor) to the input of the “NCD Dashboard” node. Refer to the following image for a visual representation:
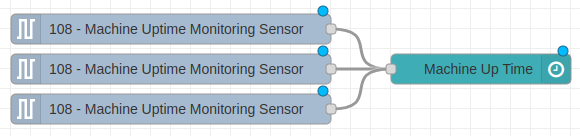
Connecting Multiple Sensors
The NCD Dashboard node is designed to handle data from several sensors simultaneously. Simply connect the output of each “Wireless Device” node to the same input of the “NCD Dashboard” node, as illustrated in the following image:
We’ll discuss how the user interface handles multiple devices in a later section.
3. Properties and Data Storage Configuration
If you double left click on the NCD Dashboard node you can open the Properties.
Name: You can assign an identifier to the NCD-Dashboard node. This name only helps distinguish your specific node within the node editor (from other nodes).
Custom Path: By default, this property is set to a fixed location. The NCD-Dashboard retrieves data from your sensor and stores it locally within Node-RED.
Data Storage: The NCD-Dashboard automatically saves the generated CSV files from the sensor(s) within the Node-RED folder.
Linux: $HOME/.node-red/log
Windows: $HOMEPATH/.node-red/log
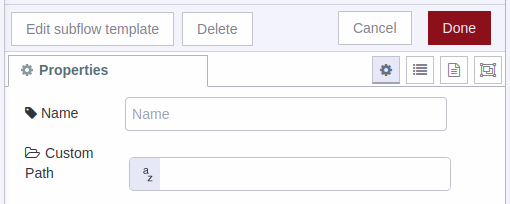
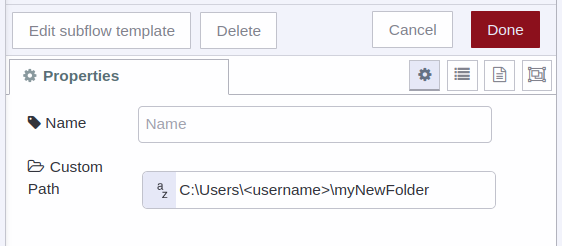
1) For PC/Windows
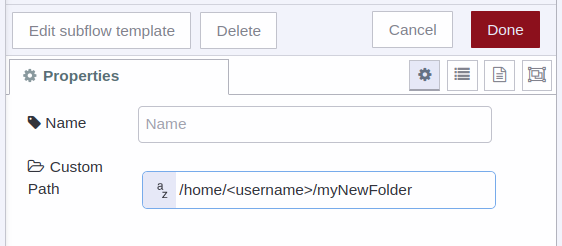
2) For Linux
4. NCD Dashboard Node Status
The NCD Dashboard nodes are designed to provide visual feedback on their operational state. This status can vary depending on the node’s input data or configuration. Here are some common scenarios you might encounter:
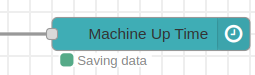
1.- If the path you enter is correct, or if you leave the property field blank (using the default path), you should see a “Saving data” status when new sensor data arrives at the node input, indicating successful storage.
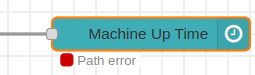
2.- It’s important to assign a valid route. If the NCD-Dashboard detects an invalid route, it will display a “Path error” message.
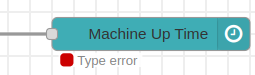
3.- If you connect a different type of NCD sensor, you will see the “Type error message”.
Remember, after making any modifications to your Node-RED flow, click the “Deploy” button located in the top right corner of the Node-RED Flow editor. This ensures your changes take effect.
Accessing
After successfully configuring and connecting your nodes, the next step is to access the user interface. This is where the NCD Dashboard elements, such as gauges, charts, and buttons, are displayed.
The procedure is as follows:
Step 1. Clic on the “Dashboard 2.0” option in the sidebar:
Step 2. Then click on the “Open Dashboard” option:
Note: In case you have deployed and cannot see the “Dashboard 2.0” content, you should reload the current page of the web browser with the “F5” key or “Reload page”.
Step 3. Your NCD Dashboard will automatically open in a new window, displaying the following elements:
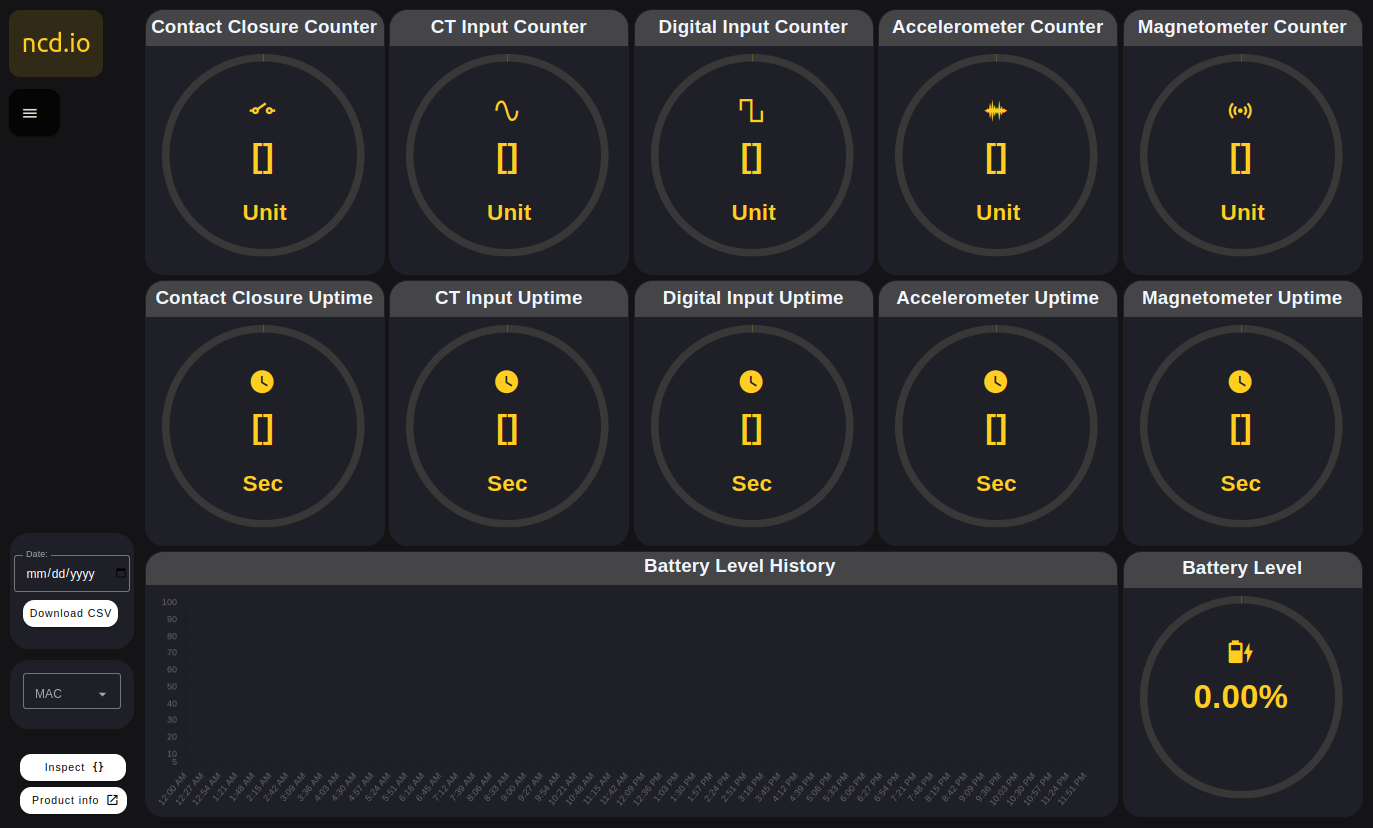
Features
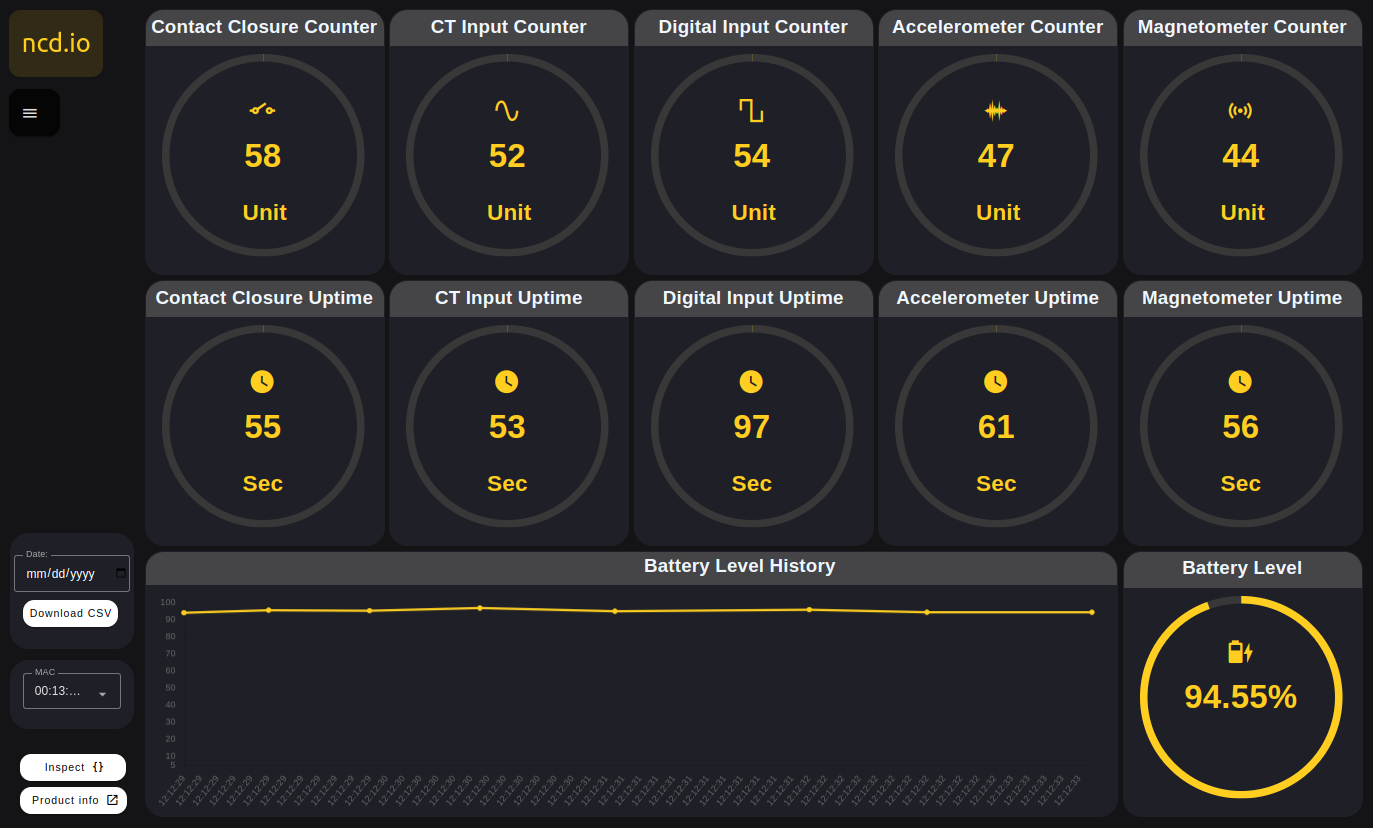
Gauges
You can display the counter and uptimer data individually by type of probe (Digital Inputs, Current (CT), Accelerometer and Magnetometer), the units of measurement are; unit and seconds.
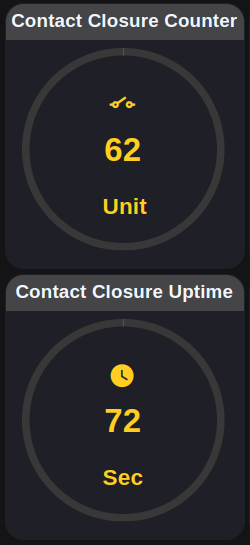
Contact Closure Input
Real-time visualization of sensor data triggered by contact closure
Current Input
Real-time machine uptime calculation based on current sensor readings
Digital Input
Real-time machine uptime visualization triggered by digital input
Accelerometer Input
Acceleration Motion Detection based Uptime calculator
Magnetometer Input
Magnetic Field Detection based Uptime calculator
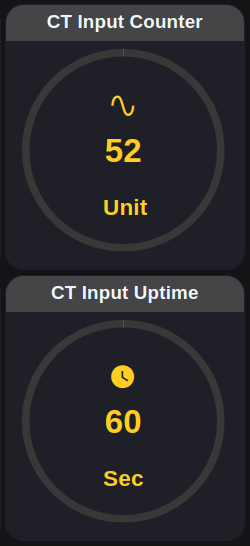
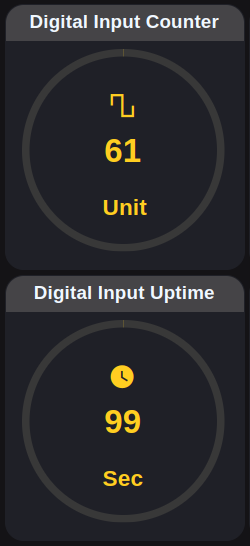
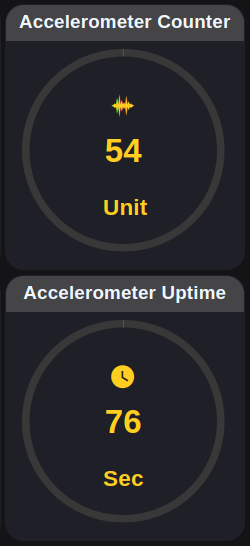
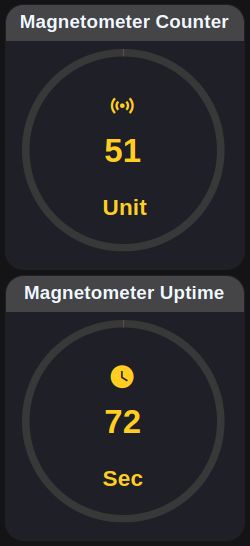
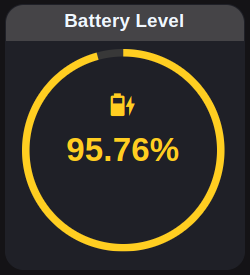
Battery Percentage
A battery level and electric current indicator is also incorporated.
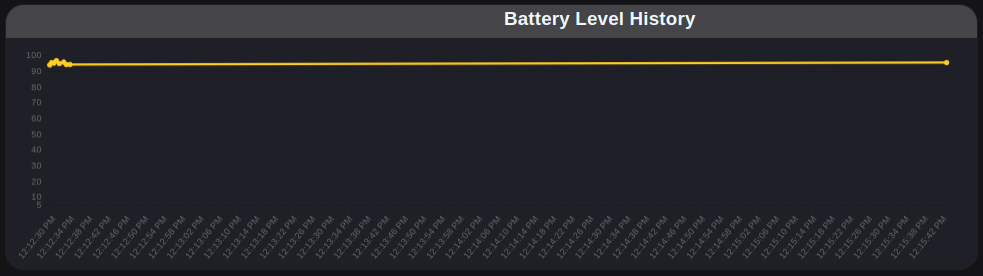
Battery Chart
Historical data for the electric current and battery level variables.
Main Menu
This menu facilitates switching between different NCD-Dashboards within the user interface (UI). This functionality is particularly useful if you have configured multiple NCD Dashboards to monitor various sensors or processes.
For example if you have configured an 2ch-ncd-dashboard and you import an ncd-Thermocouple-dashboard you will be able to navigate between the NCD-Dashboards from the main menu.
An example of this process is ilustrated in the following GIF:
DatePicker & CSV Download
The NCD Dashboard allows you to directly download locally stored CSV files containing historical data from your NCD Sensors through your web browser.
Step 1.- To display the date picker you must click on the icon on the right side of the “Date:” box.
Step 2.- Then select the date of interest:
Locate the download section in the bottom left corner. It features two fields:
- Date: Enter the desired date (format: mm/dd/yyyy) to download the corresponding CSV file containing historical sensor data for that specific day.
- Download CSV Button: Click this button to initiate the download of the CSV file directly to your web browser.
Date Format:
- mm: Represents the month (e.g., 01 for January, 12 for December).
- dd: Represents the day of the month (e.g., 01 for the first, 31 for the last day of the month).
- yyyy: Represents the four-digit year.
Step 3.- Then click on the “Download CSV” button. If the NCD-Dashboard finds the file for that date, you should be able to see the download begin (indicated by your web browser’s download icon) as shown in image.
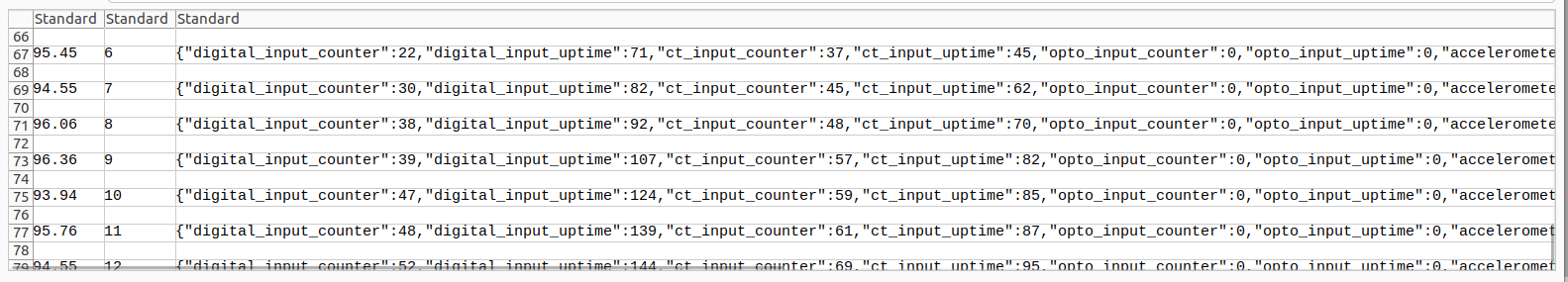
Step 4.- You can open the downloaded CSV file. The content will be similar to the following:
In case you enter a date of interest, which there is no CSV file generated, and press the “Download CSV” button, you will see the following message:
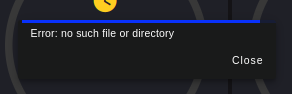
IMPORTANT
CSV file download is currently only available for the default data storage option (local in the path “./node-red”).
MAC Address Dropdown
The NCD-Dashboard provides a dropdown menu that allows you to select the ncd sensor of interest for loading, displaying, and storing its variables based on its MAC address.
When you connect a new NCD sensor to the NCD-Dashboard node, a pop-up window appears indicating a new device connection. This sensor will automatically be available for selection in the MAC Address dropdown.
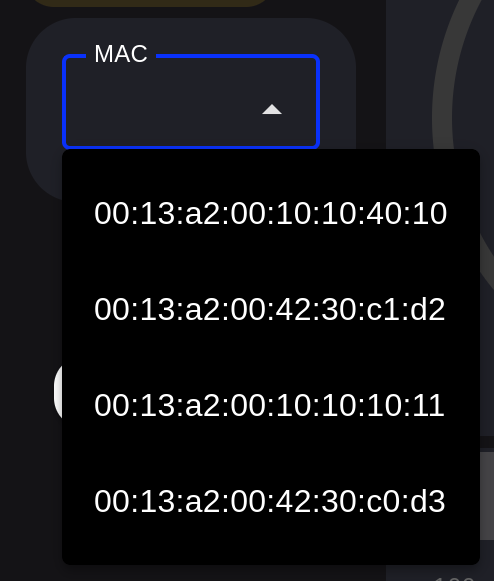
An example of this process is shown in the following image:
Inspect
By pressing this Inspect Button it is possible to access the information received from the sensor (Payload, NodeID, Firmware version, battery voltage, sensor type, MAC address, etc.), if pressed again it returns to the graphs and indicators view.
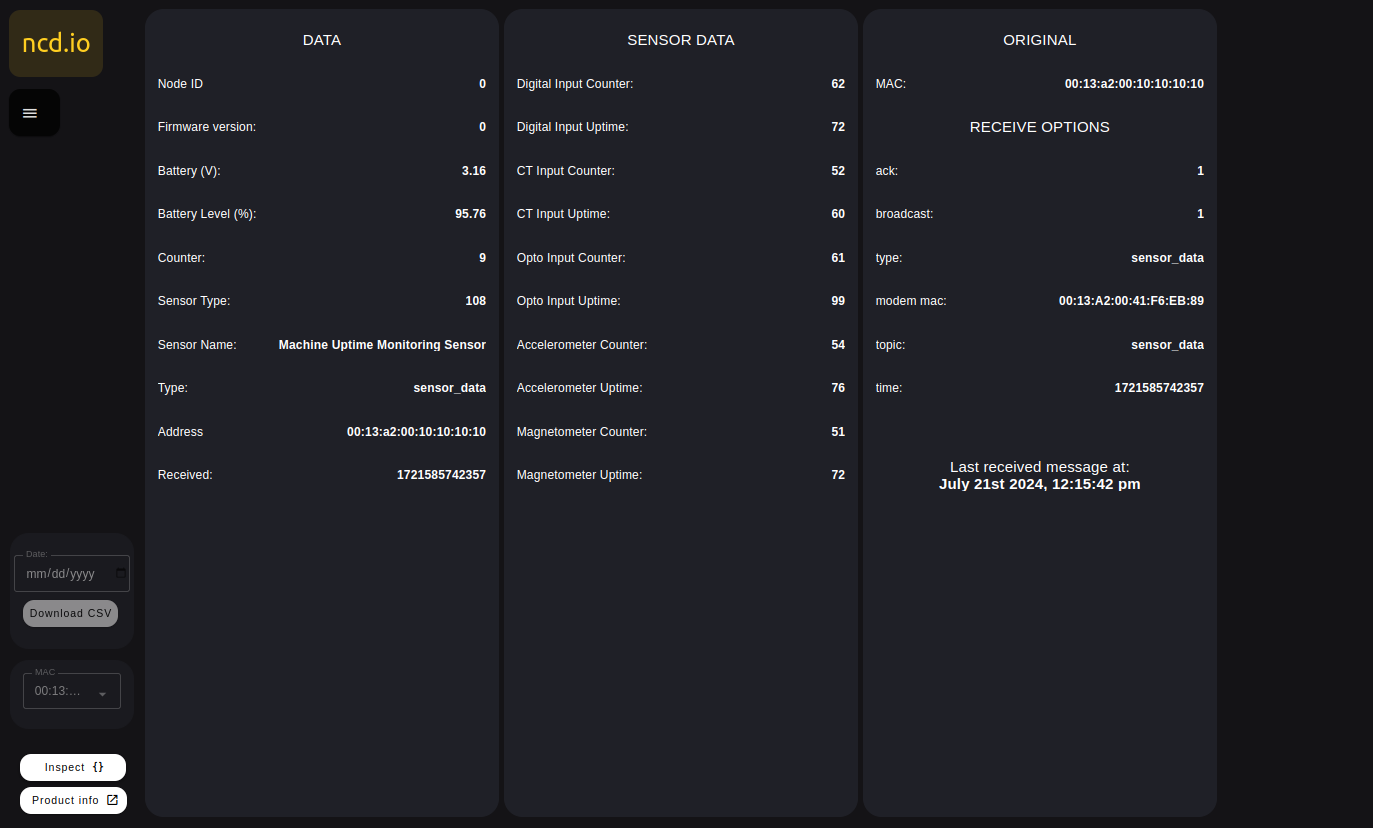
Working With Two or More ncd-dashboards In Same Node-RED Project
This instructions refers to the scenario where you have previously installed and configured an ncd-dashboard (subflow) and you want to import another ncd-dashboard (subflow) to the same project.
The procedure is the same as mentioned above, with the simple difference that as soon as you press the import button in the “Import nodes” window you will see the following message at the top of our Node-RED flow editor:
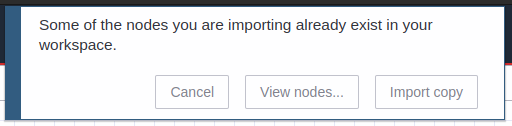
This indicates that you are importing a subflow that contains one or more nodes that already exist in your current project (workspace). Specifically it refers to the configuration node “ncd-ui-base” which represents the base configuration of all our ncd-dashboards, simply click on the “Import copy” option. This shows us the detail of the elements that were imported in our project.
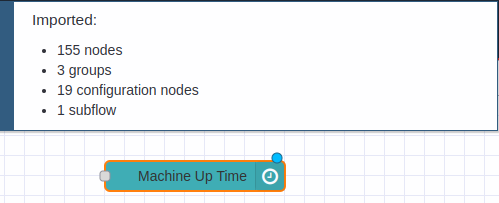
If everything is correct, the next step is to deploy in order to apply and execute the changes in our project, using the “Deploy” button:
Now, if you go to the “Dashboard 2.0” tab and click on “Open Dashboard” or simply refresh the dashboard browser tab, you will see in the main dashboard menu the new imported ncd dashboard:
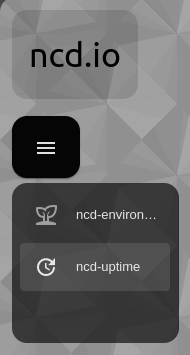
View from ncd-uptime-dashboard

View from ncd-environment-dashboard
Import Subflow to an Existent Dashboard 2.0 Project
This procedure refers to the scenario where you already have a dashboard 2.0 configured and you want to import an ncd-dashboard within the same Node-RED project.
For example, if you already have a dashboad 2.0 configured with some elements, in the dashboard you would have something like the following:
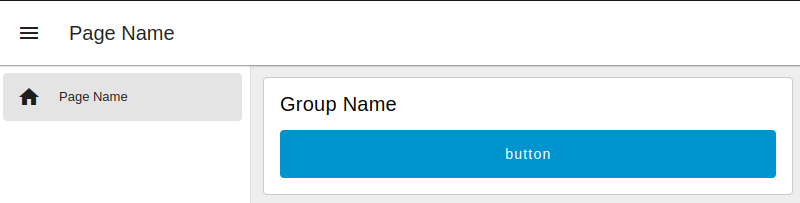
To import an ncd-dashboard to your existing project you use the same steps mentioned above; copy the JSON file from the GitHub repository, use the import window (or Key shortcut Ctrl-i), paste the JSON and click on import, the imported elements will be shown at the top, but if you deploy inside the dashboard 2.0 you will have the following message:
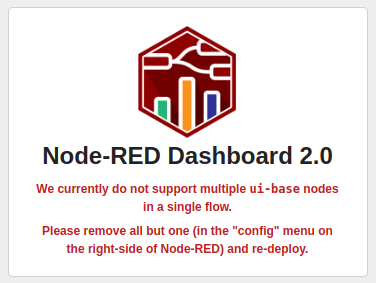
- To solve this you must return to the Node-RED flow editor, go to the “dashboard 2.0” tab and inside “Layout” you will be able to see something like the following:
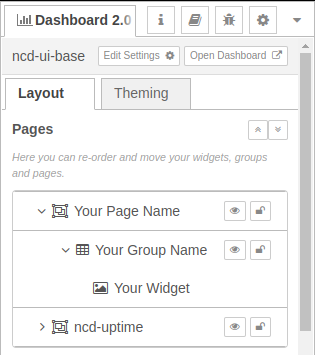
Note: You can identify the ui-pages of the ncd-dashboard by the fact that they are preceded by “ncd”.
2. Next to the “Your Page Name” identifier, if you hover the cursor you will see the “Edit” button, click on it:
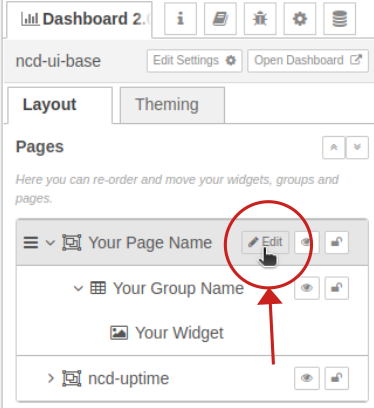
3. This opens the page configuration window, in the UI property you will click on the “Edit” (pencil icon).
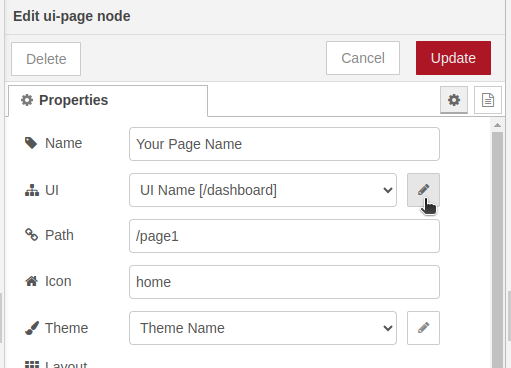
4. Now the configuration window of the “ui-base” configuration node opens, you should click on the “Delete” button (located in the upper left part of the window):
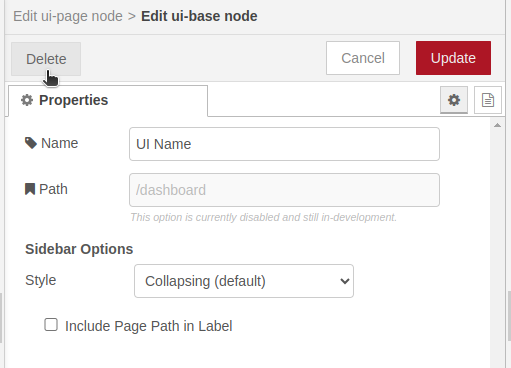
Automatically it returns to the ui-page window, and it shows us the box of the property “UI” with the outline in red color:
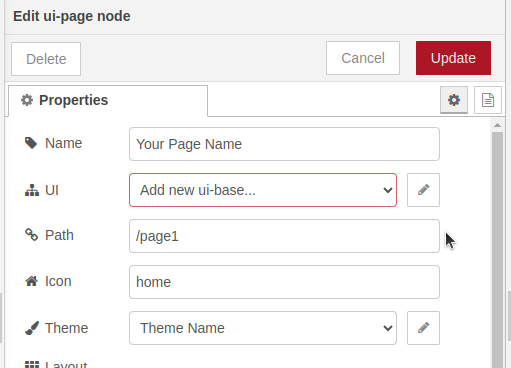
5. Click on the arrow and then select the property “ncd-ui-base[/dashboard]”:
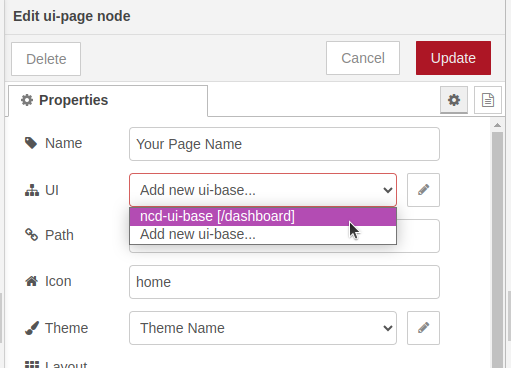
6. Finally click on the “Update” button at the top right of the window:
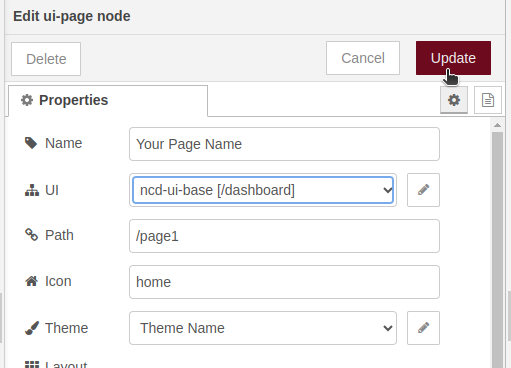
Note: This same procedure must be done if you have two or more pages previously configured in dashboard 2.0.
7. Now click on deploy button to apply the changes made to the project:
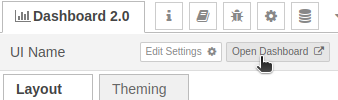
8. Go to the “Dashboard 2.0” tab and click on the “Open Dashboard” button.
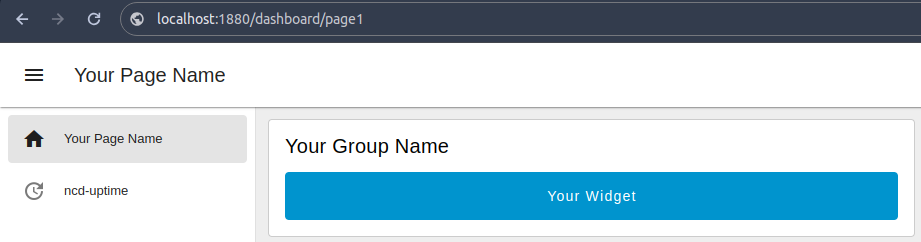
9. You will notice that the ncd-dashboard identifier has been added to the dashboard 2.0 main menu:
Possible Drawbacks During Subflow Import
1.- Import Subflow Without Dependencies Installed
If you import the flow without having previously installed Dashboard 2, you will get a message like the following:
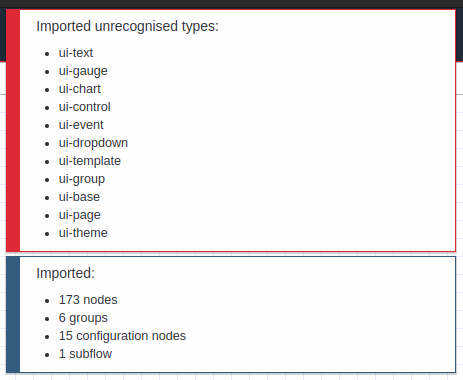
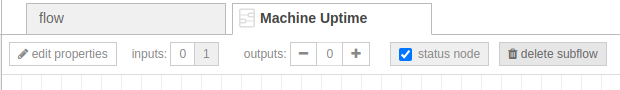
So you must delete the subflow and install the module “@flowfuse/node-red-dashboard” as mentioned at the beginning, and repeat the process. To delete the subflow you must double-click on the subflow in the Node-RED node editor to open its properties, then click on the “Delete” button at the top of the window.
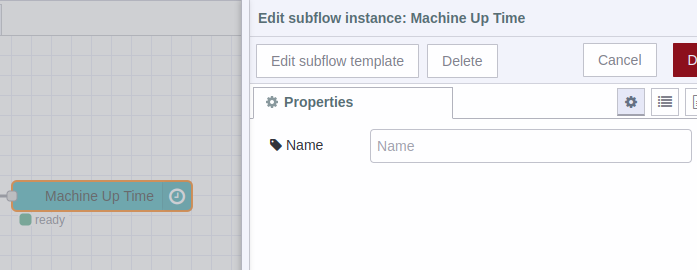
You must also delete the subflow node from the node palette in the “NCD” or “Sublows” group, double click on the node.
This opens the subflow window, at the top click on the “delete subflow” button:
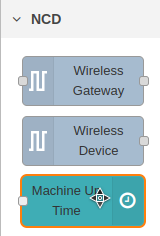
2.- Import the Same Subflow Twice / Delete Subflow
In case by mistake or by some procedure you have imported twice the same subflow, or you simply want to remove an ncd-dashboard subflow from the nodes palette, you must follow this quite simple procedure.
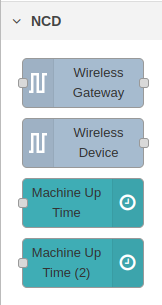
(1) Double click on the subflow node you wish to delete, the ncd-dashboard subflows are located in the node palette within the NCD group.
(2) Once the “Edit subflow template” tab opens at the top, click on the “delete subflow” button.
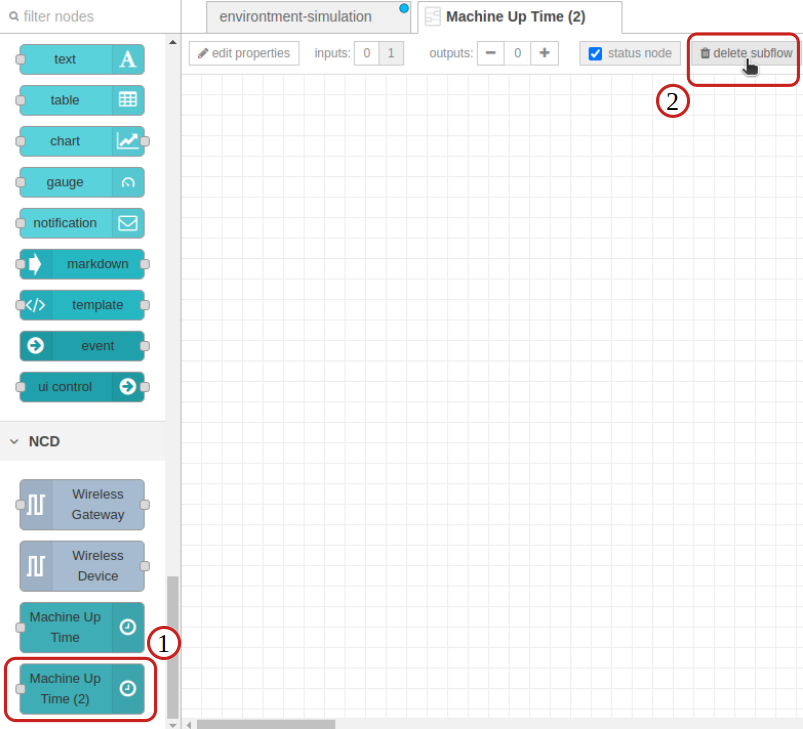
This completely removes the subflow, as well as the associated configuration nodes, you will notice that it no longer appears in the nodes palette.

Do not forget to deploy in order to save and apply the changes made to your project.
Summary
The process of machine uptime monitoring involves real-time data collection from sensors and IoT devices installed on machines. The machine uptime monitoring sensor, which leverages advanced digital inputs, current sensing technology, acceleration sensing and magnetic field measurement capabilities, provides comprehensive information on machine performance. The sensor ensures reliable data collection in a variety of industrial environments. In addition, its versatile compatibility allows seamless integration with any cloud platform, local PC or server for centralized monitoring and analysis. With this approach in mind, we developed this Dashboard packaged in a Subflow, which allows us to incorporate it into Node-RED to start visualizing the provided data in an easy and intuitive way.
Thanks.
Eduardo M.
Share this on:
You might also like:
Case Study: How North American building materials company Achieved Total Asset Visibility and Cut Recurring Costs
Case Study: From “Flying Blind” to Total Visibility: Digitizing Cosmetics Manufacturing with NCD and Ubidots

C1D2 Hazardous Environment Air Quality Sensor Quick Start Guide

C1D2 Hazardous Environment Air Quality Sensor API Overview

C1D2 Hazardous Environment Air Quality Sensor Datasheet




