Introduction
In this guide, we will demonstrate how to perform the firmware update process on an NCD Sensor using the NCD Library and Node-RED with OTA (Over-the-Air) functionality.
This method allows you to update the firmware without requiring physical access to the sensor(s). It is particularly useful for scenarios where you need to update the firmware of one or multiple devices.
The process is straightforward:
- Import an example flow into your Node-RED workspace.
- Configure the necessary parameters.
- Access the FIRMWARE.ncd file—either locally or directly from the repository.
- Enter the MAC Address(es) of the target device(s).
- Wait for the firmware upload process to complete.
Overview
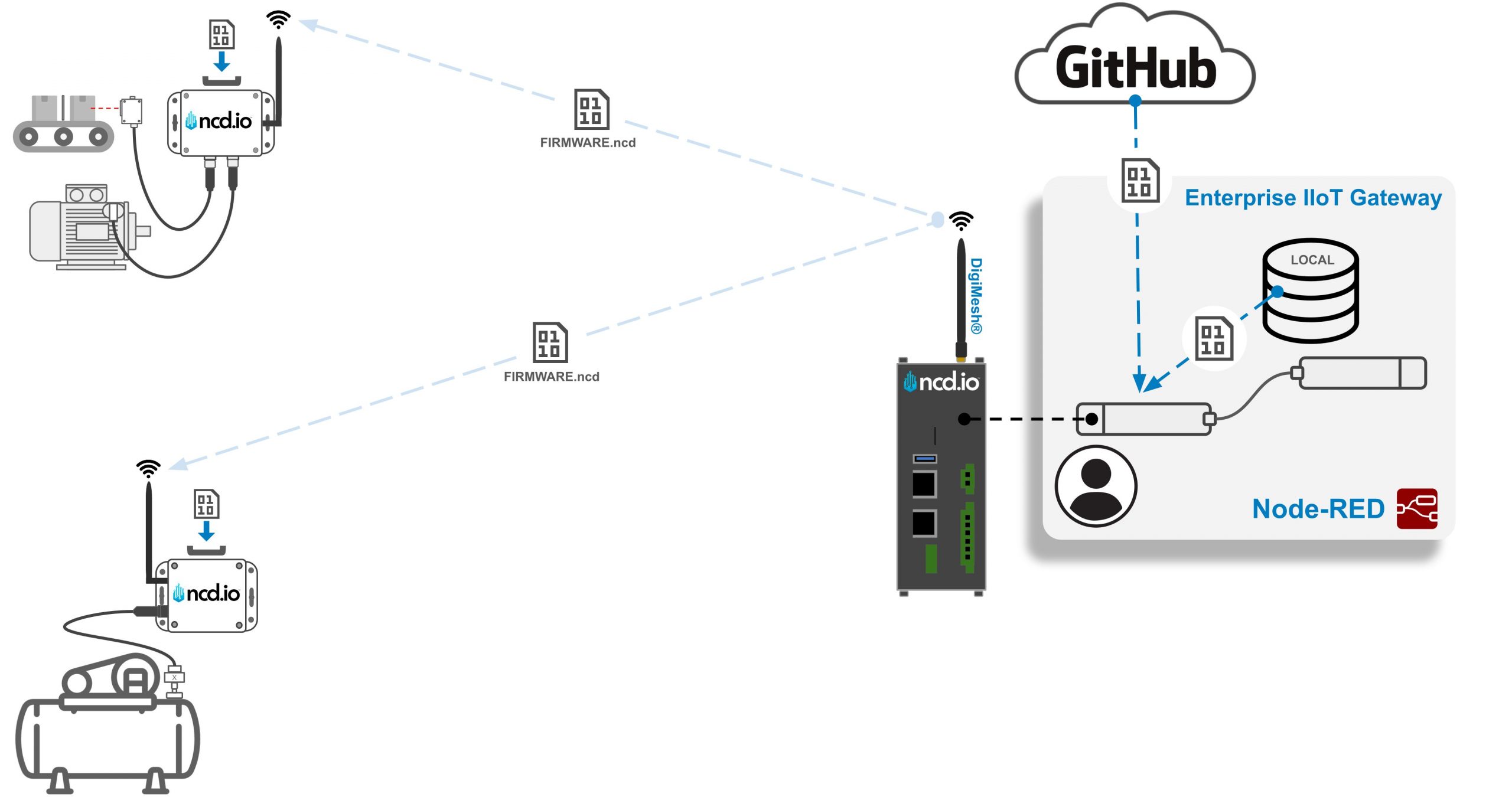
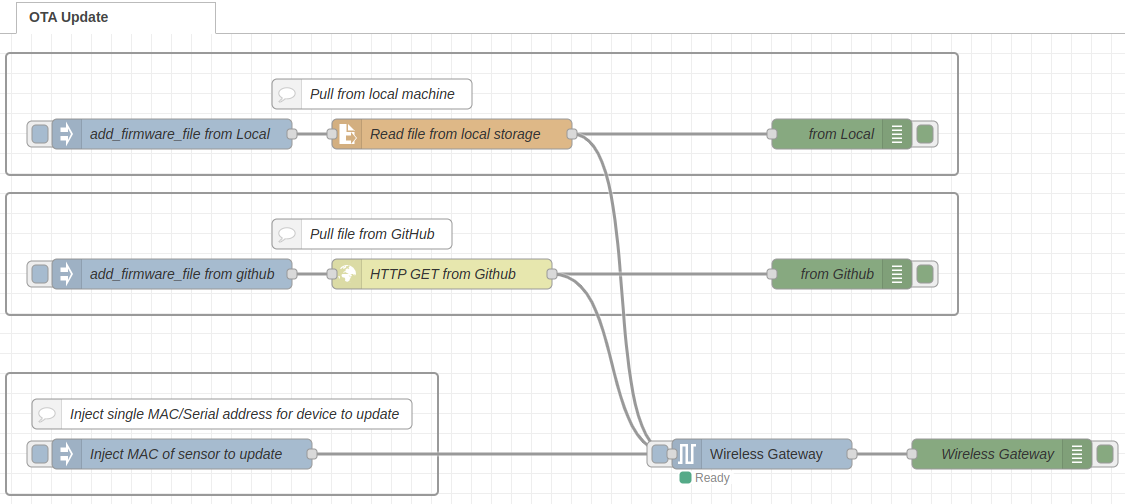
The following is a graphical representation of the firmware update process. In this flow within Node-RED, a ‘FIRMWARE.ncd’ file is accessed from either a local or a remote location. Once the file is located and downloaded, the MAC address(es) of the target field device(s) is specified. This address(es) is then passed into the Wireless Gateway node, which, after a validation process, waits for a FLY message from the corresponding sensor. Upon receiving the FLY message, the firmware update starts automatically.
Requirements
To carry out this procedure, you likely already have an NCD Sensor(s) that you wish to update the firmware. To perform the firmware update, an Enterprise IIoT Gateway or an Industrial Wireless Modem in either the Ethernet or USB version is required. It is also highly probable that you already possess one of these devices.
If you do not have one of these devices, you can find them listed below:
If you are still unsure whether your application requires a Gateway or a Modem, you can find a comprehensive guide on the differences between these two devices below:
To carry out this procedure, it is essential to have an instance of Node-RED installed and running, as well as our Enterprise NCD library. Our Enterprise IIoT Gateway and Enterprise IIoT Gateway Lite come with a pre-installed, ready-to-use instance of Node-RED, along with the library and a basic flow available. If you are using an Industrial Wireless Modem, you will need to manually install Node-RED on a PC to which the modem is connected. Here is a guide on how to install Node-RED and the NCD Enterprise library on a Windows PC:
Node-RED
Node-RED is a visual programming tool that provides a browser-based editor for creating applications by connecting predefined functions (nodes). Despite its technical nature, Node-RED offers a user-friendly interface. As an open-source project under the OpenJS Foundation, it is free to use with no subscription fees. You can install and run Node-RED locally on your PC, or, in the case of our Enterprise IIoT Gateway, it comes pre-installed and operates as a service. Node-RED, in conjunction with our Enterprise NCD library, forms a powerful tool for acquiring, managing, configuring, and uploading firmware through an intuitive interface. This combination offers a streamlined approach to optimizing the setup, configuration, and management of NCD sensor data.
NCD Enterprise Library
This library facilitates communication with and configuration of the NCD Wireless Sensor Line. It can be employed in conjunction with Node-RED to communicate and manage a Wireless Sensor Network using the Node-RED flow-based development tool on any platform. Additionally, as demonstrated, the library acts as an interface for uploading Firmware Updates to NCD Sensors. As mentioned earlier, this library is pre-installed on the Enterprise IIoT Gateway and is ready for immediate deployment.
Accessing to Node-RED
To set up and connect the NCD sensor with the Enterprise IIoT Gateway and access the Node-RED interface, please refer to the following article:
NCD Basic Node-RED Flow
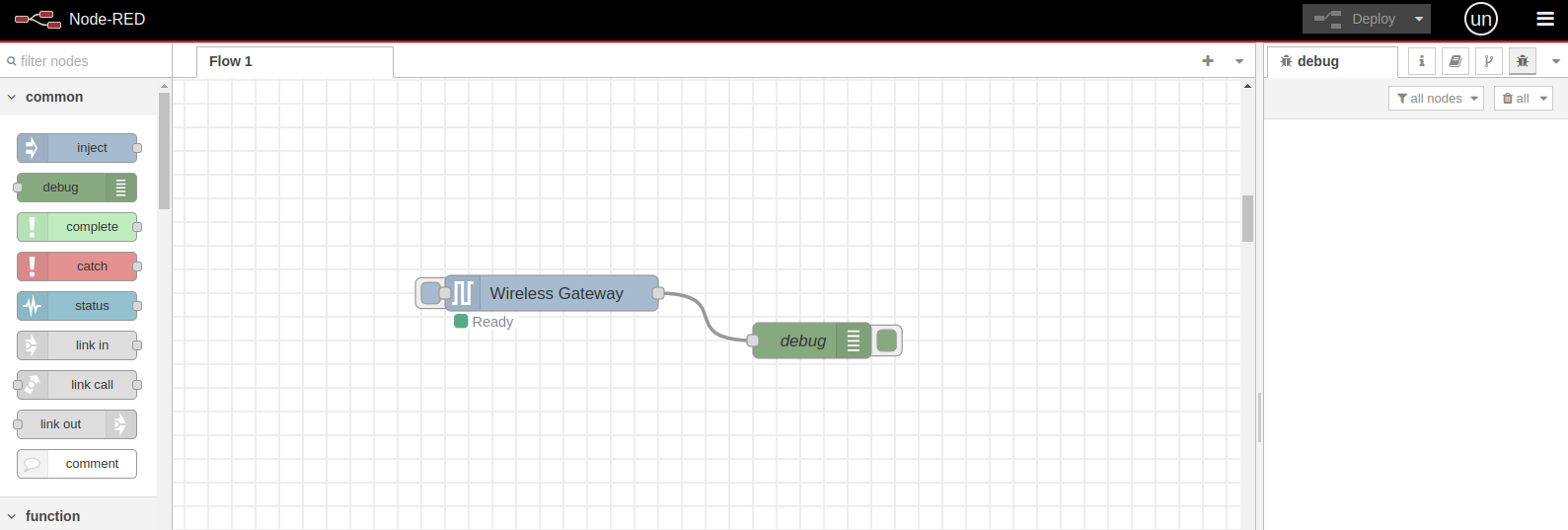
This is a preconfigured flow, meaning it is ready to receive data from the NCD sensors. When a new NCD sensor connects to the wireless network and sends data, the “Wireless Gateway” node automatically receives and processes the message. It then sends the message through its output terminal, and the message flows through the connection cable to the “Debug” node. This node receives the message and displays it in JSON format inside the “Debug” window on the right side of the Node-RED editor.
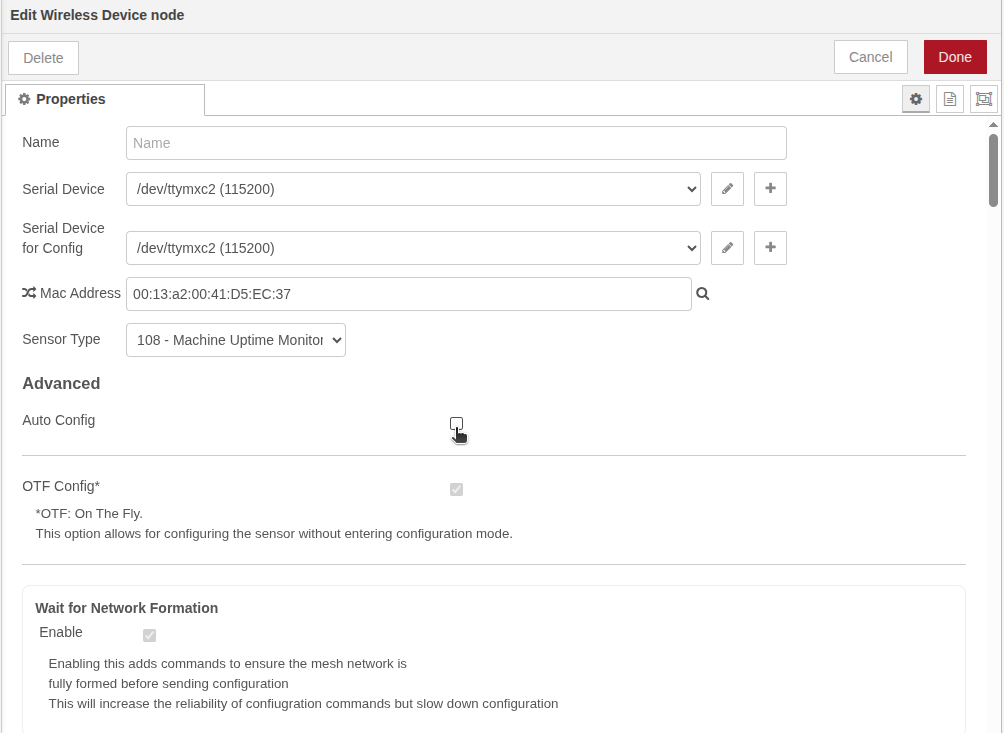
Pre-Update Check: Disabling Auto Config
IMPORTANT: Before you begin the firmware update, or anytime you perform an update, it is critically important to disable the Auto Config feature if you have a Wireless Device node associated with the NCD sensor(s) you are updating.
Why is this important?
Both the sensor configuration (via “On The Fly” -OTF) and the firmware update process are triggered by the same type message (FLY message). If both processes occur simultaneously, the configuration attempt will clash with the firmware update attempt, which will likely cause the firmware update to fail.
Firmware Update Flow
The next step is to import the flow responsible for the firmware upload. We provide two example flows for performing firmware updates:
OTA Firmware Update Single
This flow enables you to perform an over-the-air firmware update for a single NCD sensor at a time. It is particularly useful if you need to update the firmware of an individual sensor or apply different firmware updates to sensors of various types. In such cases, you will need to load the appropriate firmware for each sensor type separately. To access to the JSON file click on follow:
OTA Firmware Update Multiple
This flow allows you to perform an over-the-air firmware update on multiple NCD sensors of the same type simultaneously. It lets you specify the MAC addresses of all sensors of the same type that require the firmware update, streamlining the process for bulk updates. To access to the JSON file click on follow:
Importing Flow
This Flow is designed to work with the ‘Serial Device’ properties for the Enterprise IIoT Gateway by default. By accessing the properties of the ‘Wireless Gateway’ node, you will observe that the ‘Serial Device’ property is configured with the port ‘/dev/ttymxc2 (115200)‘.
NCD Firmware File
You need to have the “FIRMWARE.ncd” file corresponding to the version and SKU model of your NCD sensor device. This procedure allows you to upload the firmware either from a local file or by pointing to a GitHub repository in the cloud to access the “.ncd” file directly from the flow in Node-RED. Below is the GitHub repository where you can find the available “FIRMWARE.ncd” files:
Pull Method
The next step is to specify the local or remote (GitHub) path of the ‘FIRMWARE.ncd’ file that you want to upload to the NCD sensor. This flow allows you to choose between these two options.
Option 1: Pull Firmware from GitHub (Recommended)
This option is to access the ‘FIRMWARE.ncd‘ file directly from the Node-RED flow via the GitHub repository. This requires internet access from the Enterprise IIoT Gateway or from the PC if using an Industrial Wireless Modem. This approach involves specifying the URL to which the flow should point in order to locate the ‘FIRMWARE.ncd‘ file. You can obtain this URL by navigating to the GitHub repository, locating the ‘FIRMWARE.ncd‘ file specific to your NCD Sensor.
2. Then go to Node-RED and double-click on the ‘HTTP GET from Github’ node, in order to open its properties.
https://github.com/ncd-io/Enterprise-Sensor-Firmware/raw/refs/heads/main/Firmware%20Files/108%20-%20Machine%20Uptime%20Monitoring%20Sensor/V6_PR55-87.ncd
Option 2: Download Firmware and Pull from Local
1. Using the Enterprise IIoT Gateway
Let’s dive into the second method for updating your firmware: downloading the file locally and then pushing it from your computer to the Gateway. This is a fantastic option, especially if your Gateway doesn’t have internet access or is behind strict firewall restrictions.
For example, in a scenario where, for security reasons, the Enterprise IIoT Gateway can’t reach out to your PC to read or store files, we’ll need to securely push the firmware file from your computer to the Gateway using the following commands.
The process involves downloading the correct firmware file to your local PC, then securely transferring it to the Gateway using the SSH protocol. You might need to enable SSH on your Enterprise IIoT Gateway first if you haven’t already. Here’s an article that shows you how:
Step 5: Once you’ve confirmed the firmware file is in your local PC’s /Downloads directory, open Windows PowerShell. Then, type the following commands:
cd /Downloads
scp -r PRxx-xx_Vx.ncd ncdio@ncd-xxxx.local:/home/ncdio
Then click on enter key, this command might ask you for the ssh gateway password, by default is:
- ncdB3ast
Comand example:
scp -r PR63-3A_V8.ncd ncdio@ncd-c398.local:/home/ncdio
2. Using a Modem Connected to PC
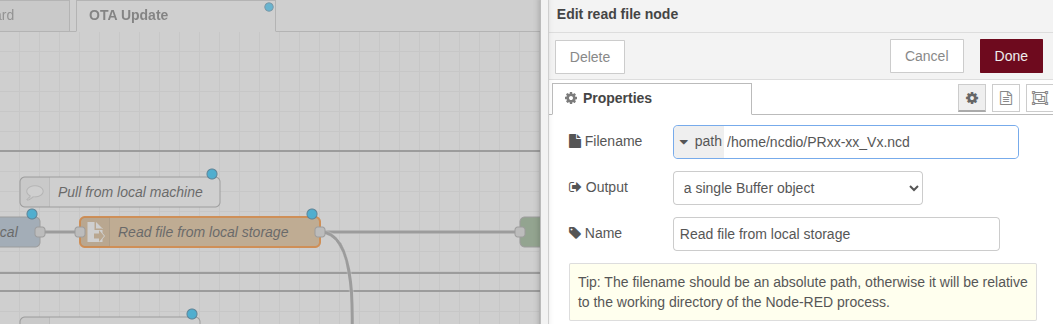
4. You will be able to view the downloaded file; you should locate the download path. This will be necessary later to specify to the Node-RED flow where to find the ‘FIRMWARE.ncd‘ file. The path corresponds to the location or directory where the file is stored on your operating system, and may look something like:
- ‘C:\Users\Username\Downloads\V4_PR55-88.ncd.’
Set the MAC Address
Once this is done, the next step is to identify the MAC address of the device to which you wish to upload the firmware. You can obtain this address from the ‘sensor_data‘ message of the sensor.
Update Single
Update Multiple
Next, access the properties of the ‘Addresses’ node by double-clicking on it. In the Address properties section, paste or enter the MAC address of each target NCD sensor, which are the devices that will receive the firmware update (you can enter from 1 up to 10 MAC addresses).
- Ready: The entered MAC address(es) are correct.
- Empty: No MAC addresses have been entered.
- Invalid length addr: Indicates that the entered MAC address has an invalid length and specifies the position of the error.
- Invalid format addr: Indicates that the entered MAC address has an invalid format and specifies the position of the error.
- Duplicate Address found: Indicates that two or more MAC addresses are duplicated and specifies the last 4 bytes of the duplicate address.
Once this is done, click the ‘DEPLOY‘ button to save and apply the changes made to the flow:
Enable Flow
To begin the firmware upload procedure with the parameters previously set, the first step is to activate the corresponding ‘Inject’ node.
1. (Apply for Option 1 – GitHub) In this case, you should activate the ‘Inject: add_firmware_file from github’ node. Similarly, upon performing this action, you will see two messages in the debug tab: one containing a buffer of the ‘FIRMWARE.ncd’ file and another from the Wireless Gateway node, indicating the status of the file and confirming that it is ready to be sent to the sensor.
5. Now, the flow will wait for the target NCD sensor to send a FLY message. Once this message is received, the Wireless Gateway node will begin the firmware upload process to the target sensor. An example of the FLY message in the debug tab is shown in the following image:
8. Finally, after the sensor restarts with the newly loaded firmware, you should see a message indicating the updated firmware version. In this case, it should show a change from an initial version 3 to version 4:
Video Demo
Summary
This article outlined the step-by-step process and necessary requirements for performing a firmware upload or update to an NCD sensor using Node-RED and our dedicated NCD library.
Thank you, NCD Team.