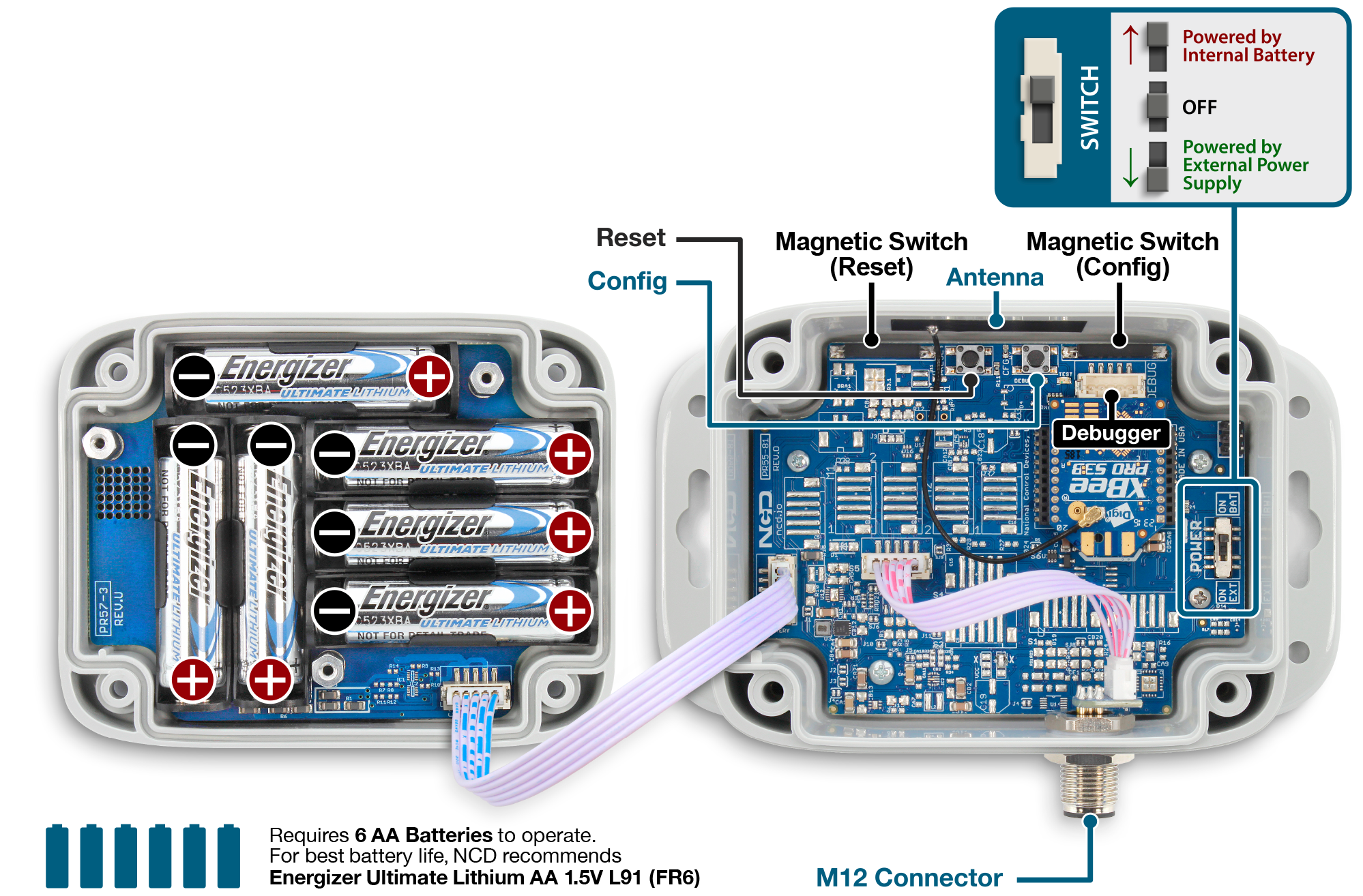
Device Overview
Primarily utilized for monitoring structural displacements, the C1D2 Industrial IoT Wireless Structural Monitoring Sensor detects movements and shifts at various structural points. Ideal for installation between footings and walls or alongside steel supports, this sensor reports any alterations in distance due to its spring-loaded cable mechanism. It is perfect for applications such as positional control, beam testing, hydraulic movement detection, and structural shift monitoring. The sensor is secured with two screws, plus an additional screw for the retractable cable, which provides analog position feedback during length changes.
Featuring a single-channel 10-bit ADC, the sensor periodically samples and wirelessly transmits data, entering a low-power sleep mode between transmissions to extend battery life. It can detect positional changes every 7 seconds (configurable), updating the cable length data if displacement varies by more than 10% (configurable). This energy-efficient operation, combined with a broad application spectrum, ensures its versatility. The sensor outputs an analog value from 0 to 1023, indicating full extension or retraction of the displacement cable.
The sensor uses a 50cm retractable wire cable, actively pulling to retract, and provides readings from 0 to 1023 as the cable extends. It should be mounted to track movements between two points, detecting linear shifts without assessing angular changes. Optimal functionality is achieved with the cable partially extended, allowing for precise detection of any length variation. However, it does not measure angular shifts, focusing solely on linear movements.
- Wireless Structural Monitoring Sensor for Structural Monitoring
- Industrial Grade IoT Displacement Sensor
- 10-bit Resolution & Precision ±0.5% FS
- Auto ADC Sample Transmission on Level Change
- Configurable 10% Analog Voltage Change Detection
- 2 Mile Line-of-Sight Range with On-Board Antenna
- Interface with Popular Cloud Platforms:
- Amazon® AWS®, Microsoft® Azure®
- Temboo, MQTT, Losant, Node-Red
- Wireless Mesh Networking using DigiMesh®
- Open Communication Protocol for Easy Software Integration
- Includes Battery Level with Every Transmission
- Validates and Retries Lost Communication Packets
Wireless Technology
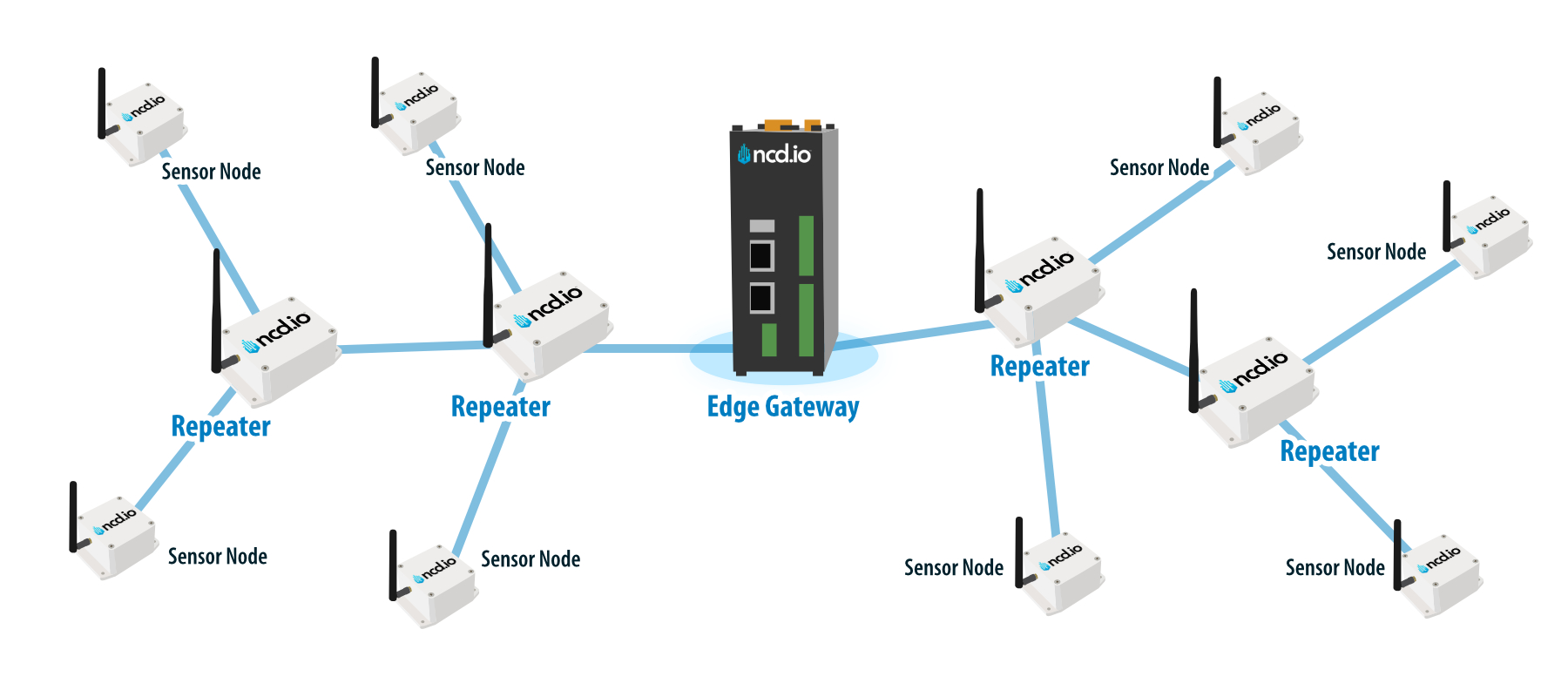
The NCD Industrial range of sensors utilizes DigiMesh, a proprietary networking technology designed by Digi® International. It is especially suitable for IIoT applications as it provides a number of benefits over conventional wireless stacks:
- Long range – up to 1200 feet in urban environments and 2 miles+ in open areas with the included antennas
- Mesh networking topology – no single point of failure, self healing network with high redundancy.
- Long battery life due to low power consumption – up to 10 years
- Simplified provisioning – extending the mesh network via repeater at no additional configuration complexity
- Works in the 868MHz, 900MHz and 2.4GHz bands – worldwide region interoperability.
If you want to learn more about DigiMesh and how it compares with another popular IoT stack (LoRaWAN) head to the article below:
IoT Wireless Sensor Networks: Digi®Mesh vs LoRaWAN®
Battery Life
| Specifications | Minimum | Nominal | Maximum | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batteries | 2 | 6 | 6 | May be Powered by 2 or 6 AA Batteries |
| Battery Life 1 TPD (TPD Transmissions per Day) | 10 Years | Battery estimation is based on a 30 min interval | ||
| Battery Life 12 TPD (TPD Transmissions per Day) | 8 Years | Battery estimation is based on a 30 min interval | ||
| Battery Life 24 TPD (TPD Transmissions per Day) | 5 Year | Battery estimation is based on a 30 min interval | ||
| Battery Life 96 TPD (TPD Transmissions per Day) | 3 Year | Battery estimation is based on a 30 min interval |
The Truth About Battery Life
Under the best of circumstances, the best non-rechargeable batteries commonly available today are limited to a 10 year non-working shelf life in a room temperature environment. Factors such as actual usage, temperature, and humidity will impact the working life. Be wary of any battery claims in excess of 10 years, as this would only apply to the most exotic and expensive batteries that are not commonly available. Also note that most battery chemistries are not rated for use in extreme temperatures. NCD only uses the best Non-Rechargeable Lithium batteries available today, which are also rated for use in extreme temperatures and have been tested by our customers in light radioactive environments. Lithium batteries offer a 10 year maximum expected shelf life due to limitations of battery technology. NCD will never rate sensor life beyond the rated shelf life of the best batteries available today, which is currently 10 years.
Applications & Use-cases
Primarily utilized for monitoring structural displacements, the C1D2 Industrial IoT Wireless Structural Monitoring Sensor detects movements and shifts at various structural points. Ideal for installation between footings and walls or alongside steel supports, this sensor reports any alterations in distance due to its spring-loaded cable mechanism. Here are some of its most common applications and use-cases.
C1D2 Industrial IoT Wireless Structural Monitoring Sensor Applications
Hazardous-Area Structural Displacement Monitoring
Class I, Division 2 areas like refineries and chemical plants can experience slow structural shifts from vibration, loading, and thermal cycling. This sensor can help track linear distance changes between two mounting points using its spring-loaded draw-wire mechanism and report displacement over NCD’s 2-mile, DigiMesh® long-range wireless network.
Steel Support and Beam Movement Trending
Steel supports and beams in hazardous process areas can deflect over time, especially around heavy equipment, pipe racks, or platforms. This sensor can help detect and trend beam/support displacement by sampling a 10-bit position signal (0–1023) and transmitting on schedule or when the reading changes beyond a configured threshold.
Hydraulic Movement Detection in Classified Zones
Hydraulic mechanisms in C1D2 locations can drift, bind, or fail to reach expected travel under load. This sensor can help verify movement by measuring draw-wire extension and automatically transmitting updates when displacement changes—supporting safer operations without running new signal wiring through hazardous areas.
Lifting and Spreader Beam Testing in Hazardous Facilities
Facilities that handle flammables often still need periodic lift/beam testing where deflection matters for safety and maintenance. This sensor can help capture displacement during tests using its retractable cable and forward results to gateways/cloud tools (including Node-RED/MQTT) for logging and review.
C1D2 Industrial IoT Wireless Structural Monitoring Sensor Use-cases
Pipe Rack Deflection Alerts During Thermal Cycling
In a Class I, Division 2 process unit, the sensor can be mounted between a pipe rack member and a stable reference point to trend small deflections as temperatures change across day/night and operating cycles. This data could be used to trigger alerts when displacement shifts beyond a configured change threshold (e.g., >10%), helping teams prioritize inspection before misalignment stresses supports or joints.
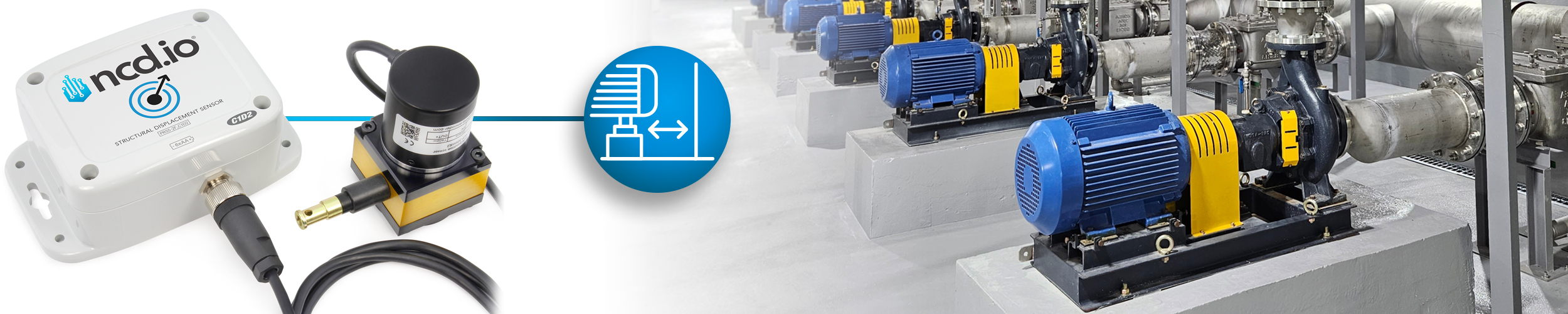
Pump Skid Settlement and Alignment Drift Monitoring
In a C1D2 pump room, the sensor can be installed between a pump skid and a nearby wall/support to monitor slow settlement or alignment drift over time. This data could be used to spot gradual baseline changes early, schedule corrective alignment, and maintain a time-stamped movement history via long-range mesh reporting.

Loading Rack Mechanical Travel Logging
At a hazardous loading rack, the sensor can be mounted to measure the travel of a mechanical stop, gate, or arm where position consistency matters during transfer operations. This data could be used to log each movement event and flag abnormal travel patterns by relying on periodic sampling (as fast as a configurable ~7 seconds) plus “send-on-change” reporting when the value shifts meaningfully.
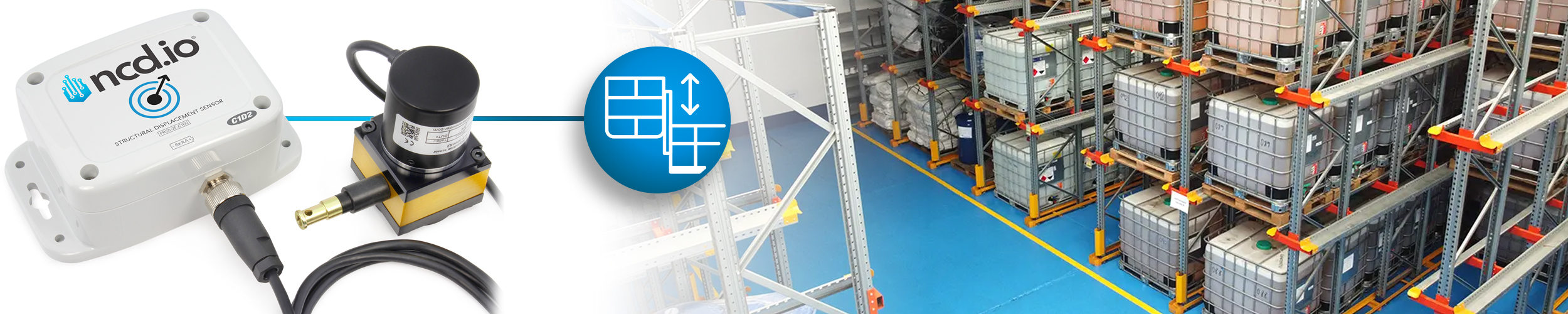

Structural Joint / Crack Movement Trending in a Classified Building Area
In a Class I, Division 2 enclosure or structure with a known joint or crack, the sensor can be mounted across two points to quantify changes in linear separation using the draw-wire cable. This data could be used to distinguish normal movement from progressive shift, providing objective evidence for maintenance and safety reviews while pushing data to common cloud/edge workflows (AWS/Azure/Node-RED/MQTT).

