
Getting Started
In this tutorial, we will show you how to receive wireless sensor data from NCD IoT sensors over a standard Ethernet connection. The photo shown above is a pre-production prototype of a simple Ethernet to wireless gateway, which will be used to receive all data over the Ethernet connection. The enclosed version of this device is on the way, but we will go ahead with our article for those who need to know more about the process.
For this tutorial, we will need a few pieces of hardware and some software to help you see data coming in from the sensor. So let’s dive in, starting with hardware and software requirements. Some basic experience with NCD sensors is preferable. Additionally, some knowledge of network communications will be helpful, but we will guide you through the basics. For the purposes of this tutorial, we will be using DHCP. While static IP addresses are supported, they will remain outside the scope of this tutorial so please make sure your router has DHCP enabled.
Hardware Requirements
- One or More NCD Wireless IoT Sensors
- PR52-8 Wireless Sensor Gateway with Power Supply (to be released)
- Available Ethernet Port on your Network
Software Requirements
Setup
Hardware setup is very straightforward. Simply plug the gateway into your network and power it up. Your gateway comes pre-configured with all necessary settings for proper operation. By default, NCD sensors come pre-configured with a wireless encryption key. This encryption key is also stored in the gateway. If you have changed the encryption key on your wireless sensors, it will be necessary to change the encryption key inside the gateway. to match. Please contact NCD technical support to if you believe you need to change the wireless encryption key.
Network Communication
In order to communicate to the wireless communications module, it will be necessary to open a port on the Ethernet communications module. The problem is, the Ethernet communications module will negotiate a IP address with your DHCP router, but you will have no idea what IP address was negotiated. Since you do not know the IP address, you cannot open a connection to the Ethernet interface. So the first order of business is to determine the IP address of the Ethernet interface of the NCD gateway on your network.
Discovering the IP Address
Since the IP address of the NCD Ethernet Gateway is currently unknown, we will help you locate the IP address in this part of the tutorial. There are three ways to determine the IP address of the NCD Ethernet Gateway on your network.
- Use Comm Operator, the Easy Way Shown in this Tutorial
- Use NCD Base Station, Requires More Software but Covered in this Tutorial
- Login to your Router and Look at the DHCP Record (Since Every Router is Different, We are Unable to Assist)
Locating the IP address of the NCD Ethernet gateway on your network is actually pretty easy. NCD Ethernet Gateways send a UDP broadcast every 30 seconds or so, which contains the IP address of the Ethernet gateway. We will use Comm Operator to listen for UDP broadcasts and sniff out the IP address of the NCD Ethernet Gateway.
Comm Operator & UDP Broadcasts
Comm Operator is a tool that can be used to communicate via TCP/IP or via a COM port for communications to NCD devices. Comm Operator was developed by Shirui Xu, a senior programmer at NCD. Nearly every product manufactured by NCD was tested using Comm Operator as part of design or order fulfillment process. Over the years, Xu has added many features that apply to the use of NCD products as well as devices manufactured by other companies. One of Comm Operators many features is to simply listen for and display UDP broadcast data. In this section, we will show you have to use Comm Operator to listen for UDP broadcasts. Comm Operator will also be used to display raw data from wireless sensors later in this tutorial. Please note that Com Operator is available for free for 30 days.
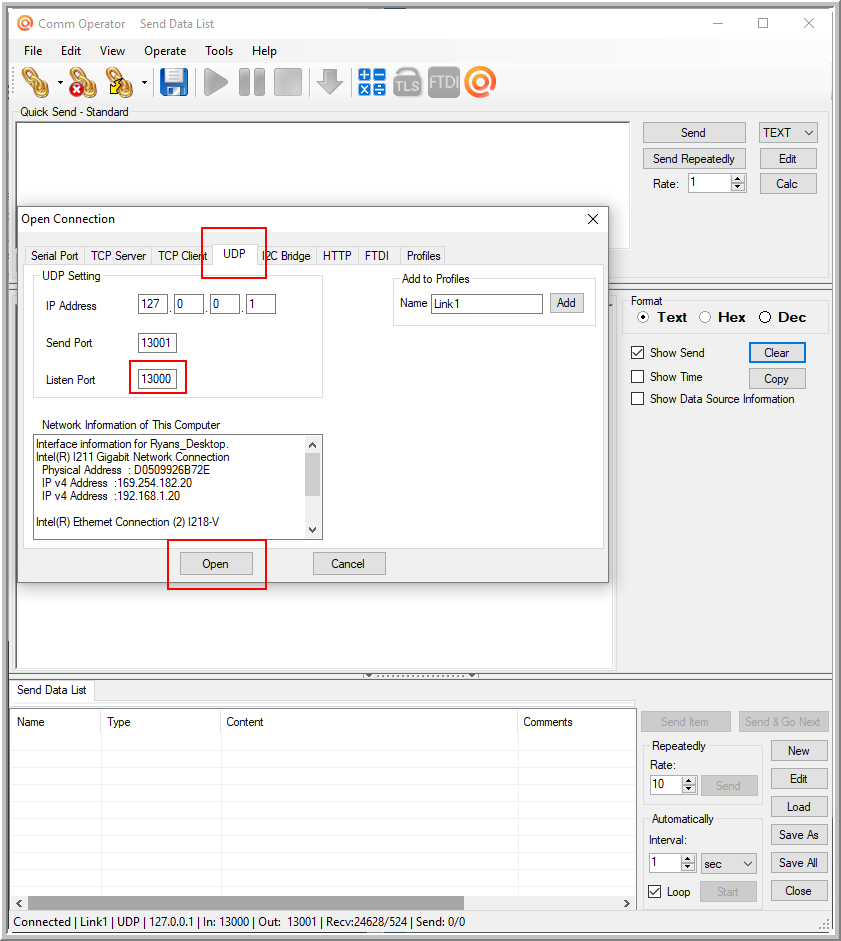
From the File pull-down menu, select “Open Connection”. This will show the above dialog box. Click on the “UDP” tab and make sure the Listen Port is set to 13000. Do not change the IP address or any other settings on this form. Select “Open”. This will instruct Comm Operator to listen for UDP broadcasts and display incoming data in the Log window.
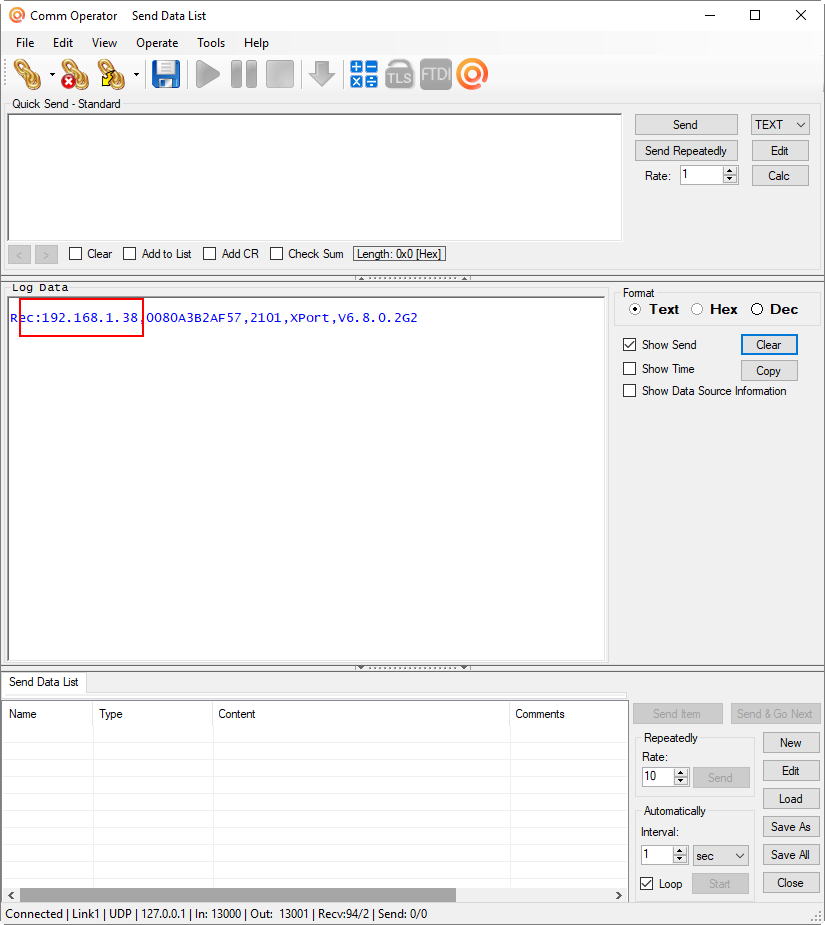
After about 30 seconds, the Log window will show data from the Ethernet interface of the NCD Ethernet Gateway. The UDP broadcast shows the IP address of the device (highlighted in Red above”, as well as the Mac Address, the Port Number 2101 (you will want to take note of this later), as will as the Model of communications module (Lantronix XPort), and the firmware version of the Lantronix XPort module.
Base Station & UDP Broadcasts
Base Station Software can also be used to see the IP Address of the NCD Ethernet Gateway. Base Station does not officially support NCD Enterprise Sensors, but the entry screen is capable of seeing and displaying the UDP broadcasts. Install Base Station from https://ncd.io/start. After running Base Station, you should see the following window:
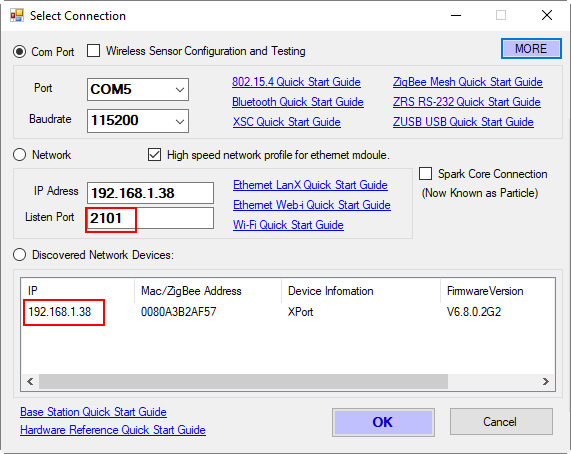
Make Sure the Listen Port is set to 2101. Within 30 seconds, the IP address of the Ethernet Wireless Gateway will be displayed.
Watching Sensor Data
Now that you have the IP Address of the Ethernet Gateway, it’s time to open a TCP/IP port and watch the data packets arrive. Data will be displayed from any and all sensors that happen to be broadcasting at the time. NCD sensors can be sent to broadcast more frequently, but every 10 minutes is a typical default broadcast interval. So the following sections may take some time. To speed things along, pressing the “Reset” button on the sensor will cause a sensor to broadcast identification and status data. Be sure to setup Comm Operator (as shown below) before pressing Reset!
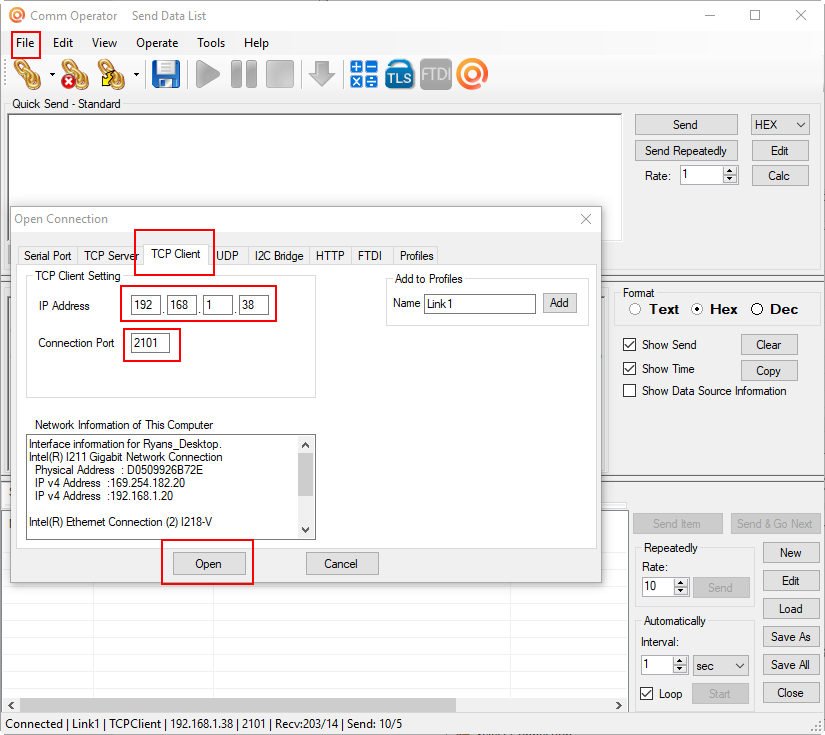
From the “File” Pull-down menu select “Open Connection” Click on the “TCP Client” tab and fill in the IP Address indicated earlier in this guide. Make sure the Connection Port is set to “2101” and click “Open”.
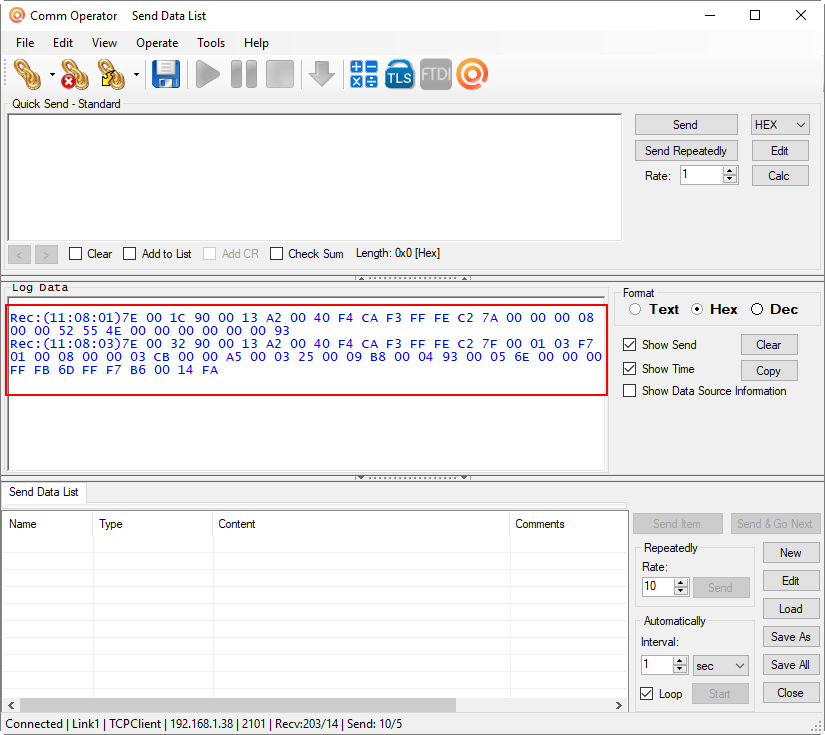
Every time the sensor transmits data, the data will be displayed in the “Log Data” window. You can manually trigger a transmission by resetting each sensor.

