Introduction
In the era of Industry 4.0, data is the new currency. However, on a typical factory floor, this currency is often locked away in “silos”—millions of data points generated by legacy machines, PLCs, and sensors that speak different languages and cannot communicate with the outside world.
This article explores the technical architecture of IIoT Gateways, demystifies the debate between Edge and Cloud computing in manufacturing, and examines how solutions like the NCD Enterprise IIoT Gateway serve as the critical infrastructure for modern industrial digitalization.
What Is an Industrial IoT Gateway?
An Industrial IoT gateway is a localized computing system that collects, stores, processes, and analyzes data at the network’s edge. It effectively alleviates the workload on cloud services and remote data centers. These gateways acquire information from diverse sensors, devices, and machinery, and subsequently deliver the pre-processed data to the cloud for comprehensive remote monitoring.
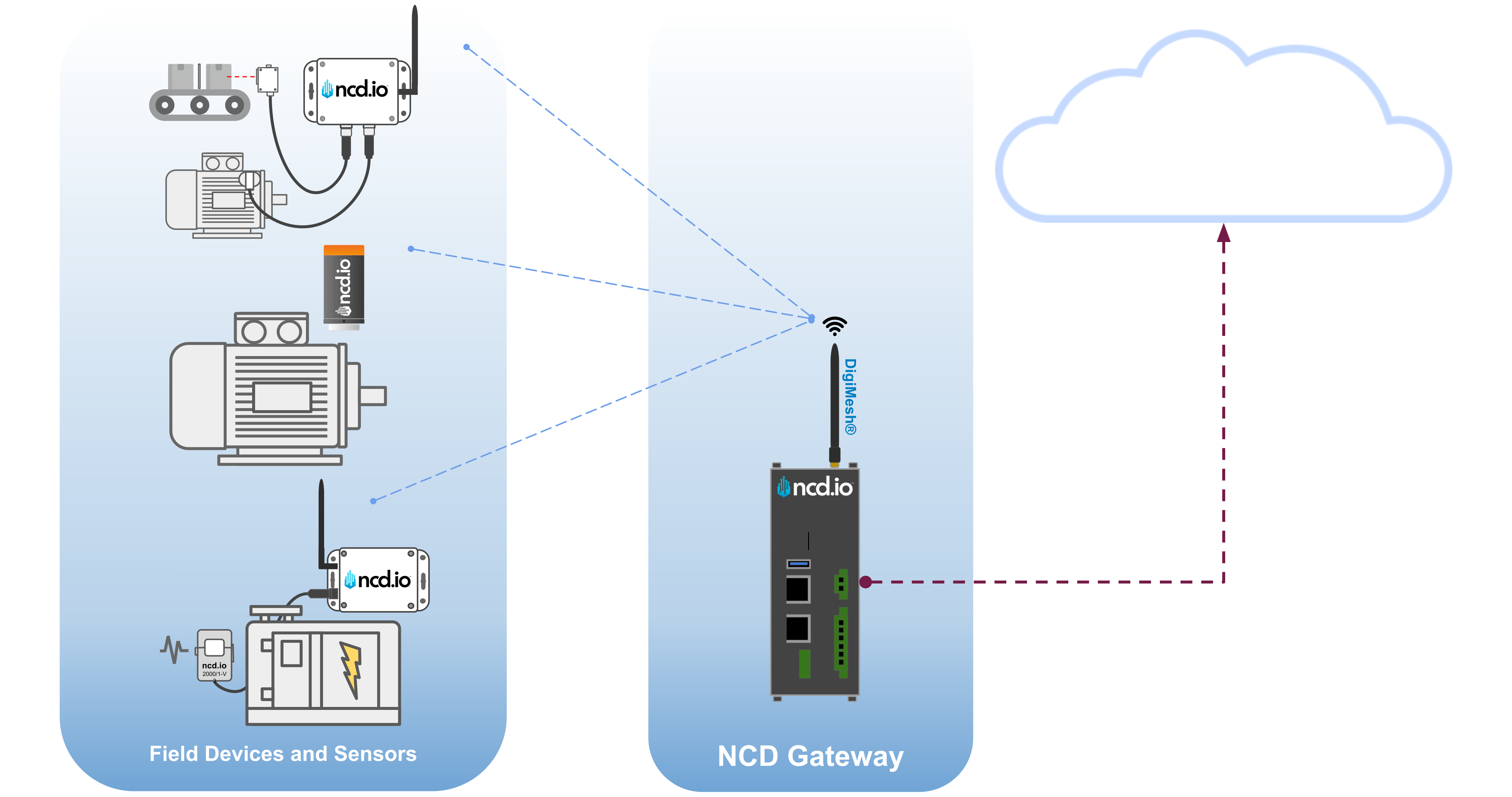
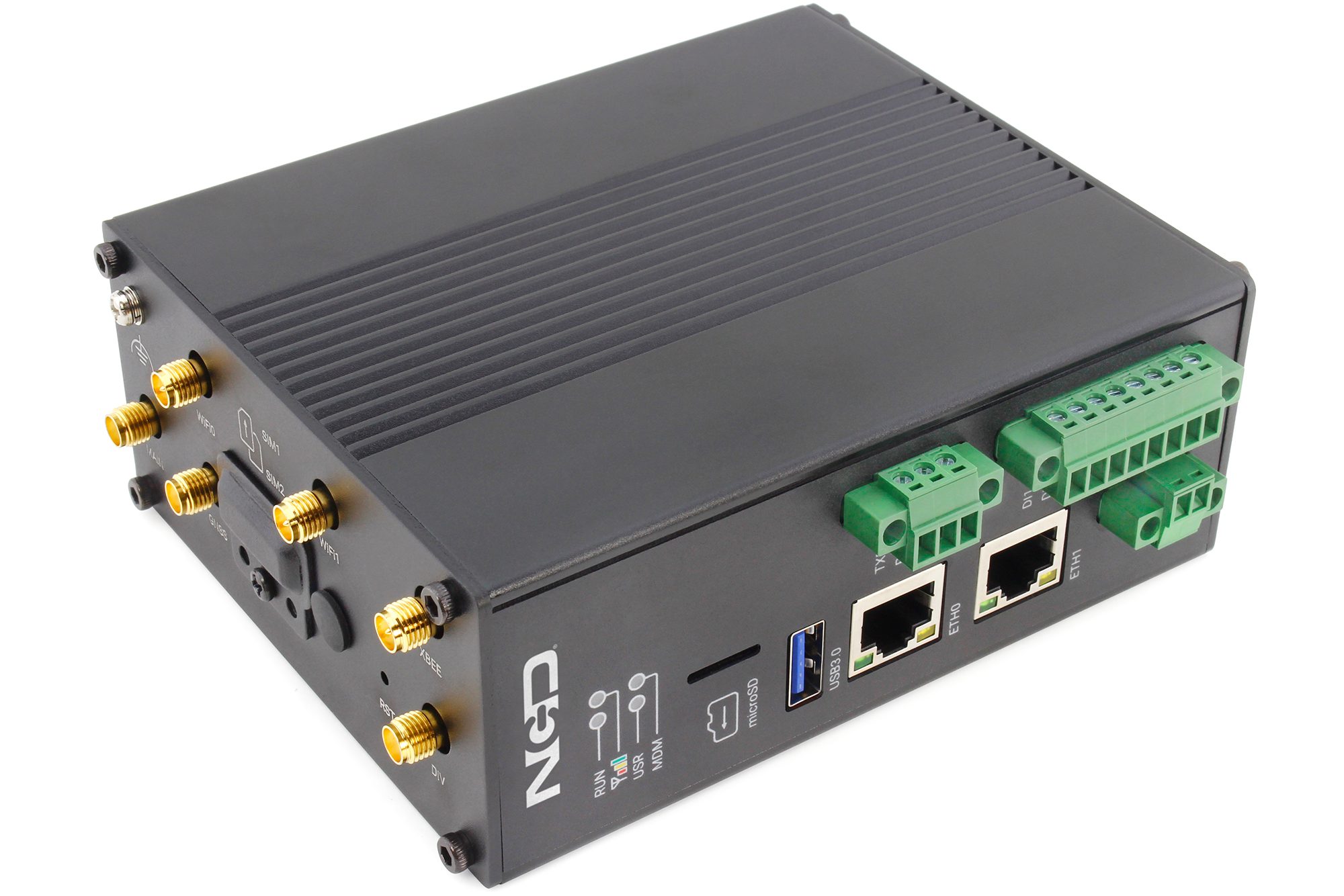
At its core, an Industrial IoT Gateway is a ruggedized hardware device that acts as a bridge between the Operational Technology (OT) on your factory floor and the Information Technology (IT) of the cloud or enterprise network.
Think of it as a universal translator and a traffic controller combined. It collects raw telemetry from diverse sources—vibration sensors, temperature probes, PLCs, and SCADA systems—translates their disparate protocols (like converting DigiMesh or Modbus to MQTT), and securely transmits this data to a destination where it can be analyzed.
Key Functions & Features
- Data Aggregation: The gateway acts as a central hub, gathering massive amounts of data from numerous NCD sensors (monitoring temperature, current, pressure, vibration) and industrial equipment.
- Protocol Conversion: It translates wireless industrial protocols (such as DigiMesh) into standard IT-friendly protocols (like MQTT, HTTP, OPC-UA) required for cloud ingestion.
- Edge Computing: Rather than just passing data along, the gateway pre-processes it locally. This allows for faster insights, reduced bandwidth usage, and real-time decision-making.
- Security: It provides a fortified boundary between the factory and the internet, utilizing encryption, authentication, and firewalls to protect sensitive production data.
- Rugged Design: Unlike a standard office router, an industrial gateway is built to withstand harsh environments, including extreme temperatures, vibration, and dust.
Edge vs. Cloud in Manufacturing
There is a common misconception that manufacturers must choose between Edge or Cloud computing. In reality, they are two distinct approaches to data management that solve different problems.
Cloud Computing
The Central Brain
Location: Remote, centralized data centers (e.g., AWS, Azure).
Cloud computing excels at the “heavy lifting.” It offers virtually unlimited storage and processing power necessary for analyzing historical data from multiple factories simultaneously.
- Best For: Deep analytics (AI/ML), demand forecasting, long-term data archiving, and enterprise-wide dashboards.
- Key Benefit: Scalability. You can spin up massive computing resources to train predictive maintenance models without buying new hardware.
Edge Computing
The Reflex System
Location: At or near the source of data (the factory floor).
In manufacturing, Edge computing is about speed and autonomy. It handles real-time, low-latency tasks. If a machine overheats, the “Edge” (the Gateway) needs to make the decision to shut it down now—not wait for a server 500 miles away to process the request.
- Best For: Real-time monitoring, immediate alerts, safety shutdowns, and local automation where milliseconds matter.
- Key Benefit: Offline reliability. If the internet goes down, the Edge gateway keeps running local logic, ensuring production continuity.
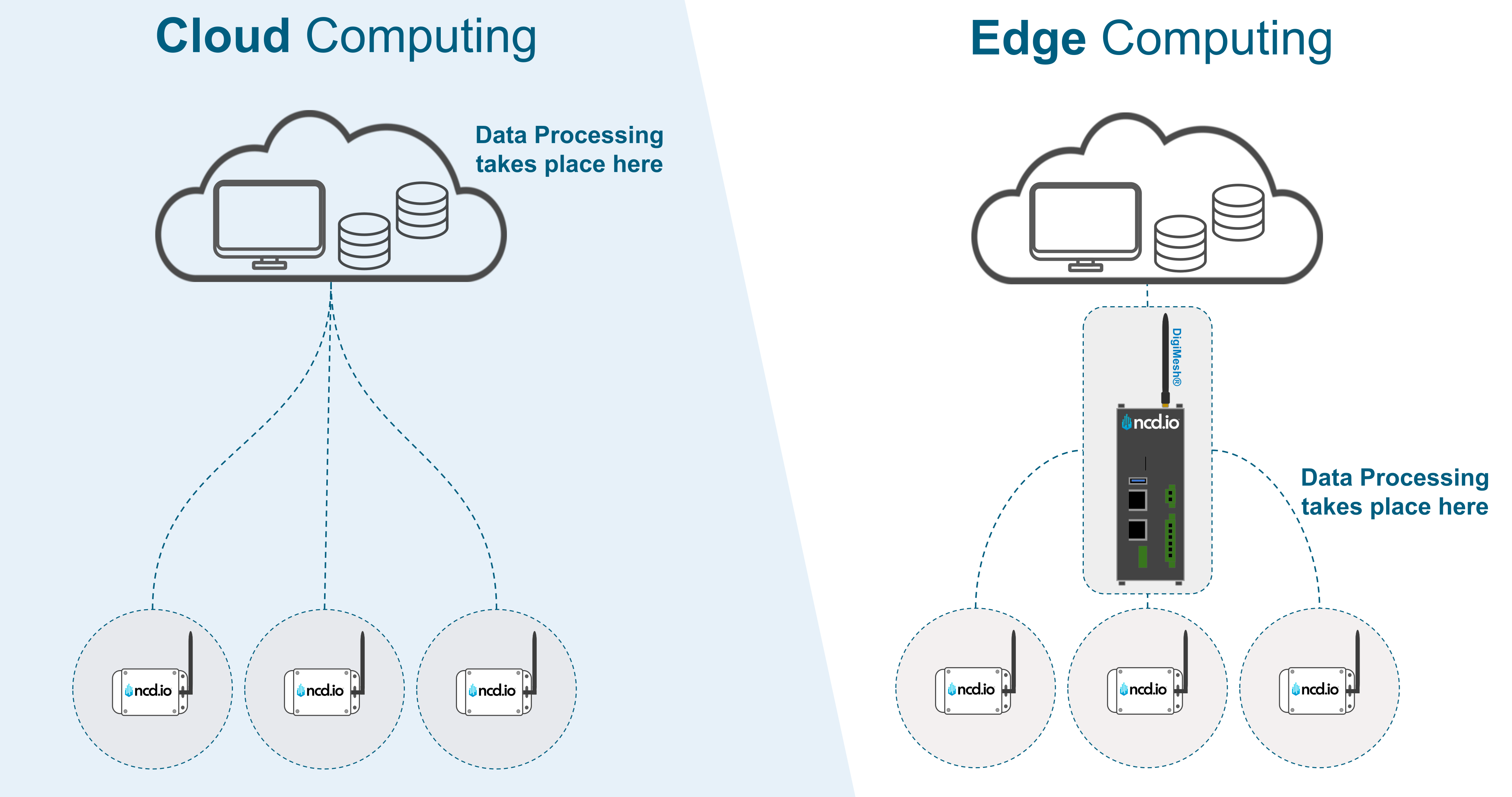
The Limitations
| Feature | Cloud Limitations | Edge Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| CONNECTIVITY | Dependent on constant internet; network drops cause data gaps or delays. | Requires local network management; less dependent on WAN. |
| LATENCY | High latency (seconds to minutes); unacceptable for safety-critical real-time control. | Ultra-low latency; limited by the processor speed of the local device. |
The Hybrid Model
The most effective Industry 4.0 strategies use a Hybrid Model. This isn’t a competition; Edge and Cloud are allies.
1. Data Collection: Sensors feed raw data to the Industrial IoT Gateway.
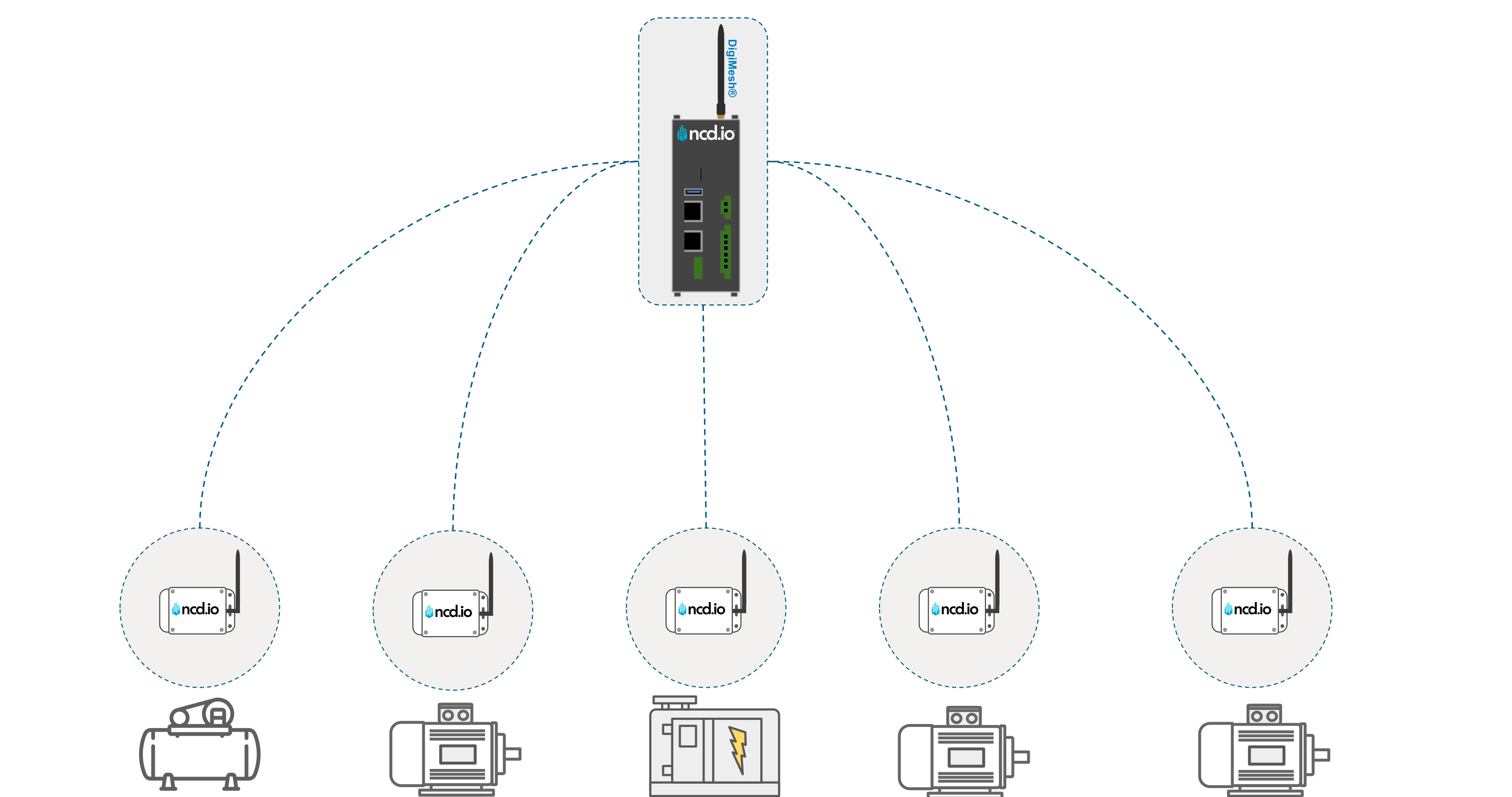
2. Edge Processing: The gateway decode and filters data value or noise (e.g., “temperature is normal”) and makes immediate decisions (e.g., “Vibration is critical! Stop machine!”).
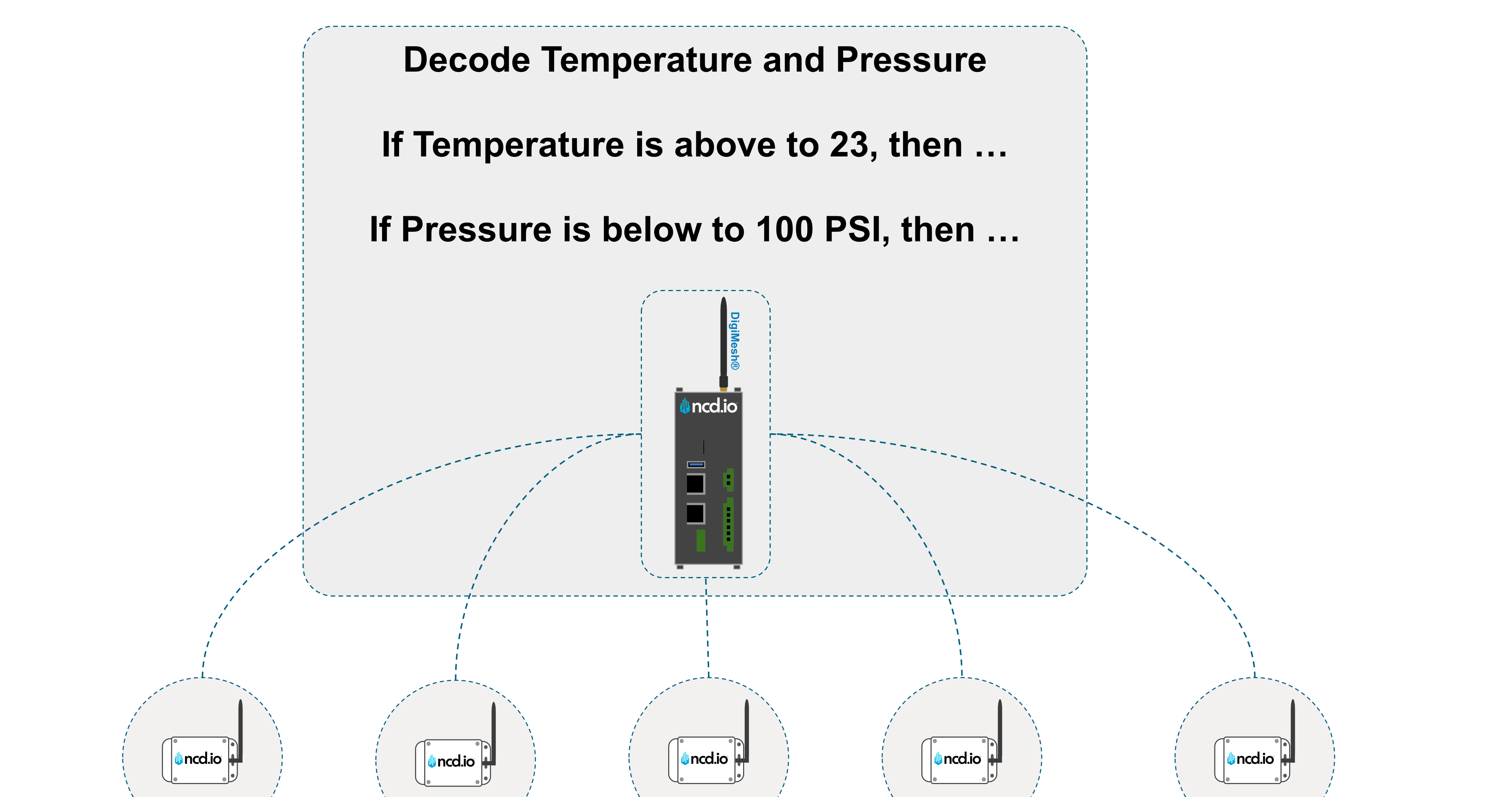
3. Cloud Transmission: Only meaningful, aggregated data is sent to the cloud, saving bandwidth costs.
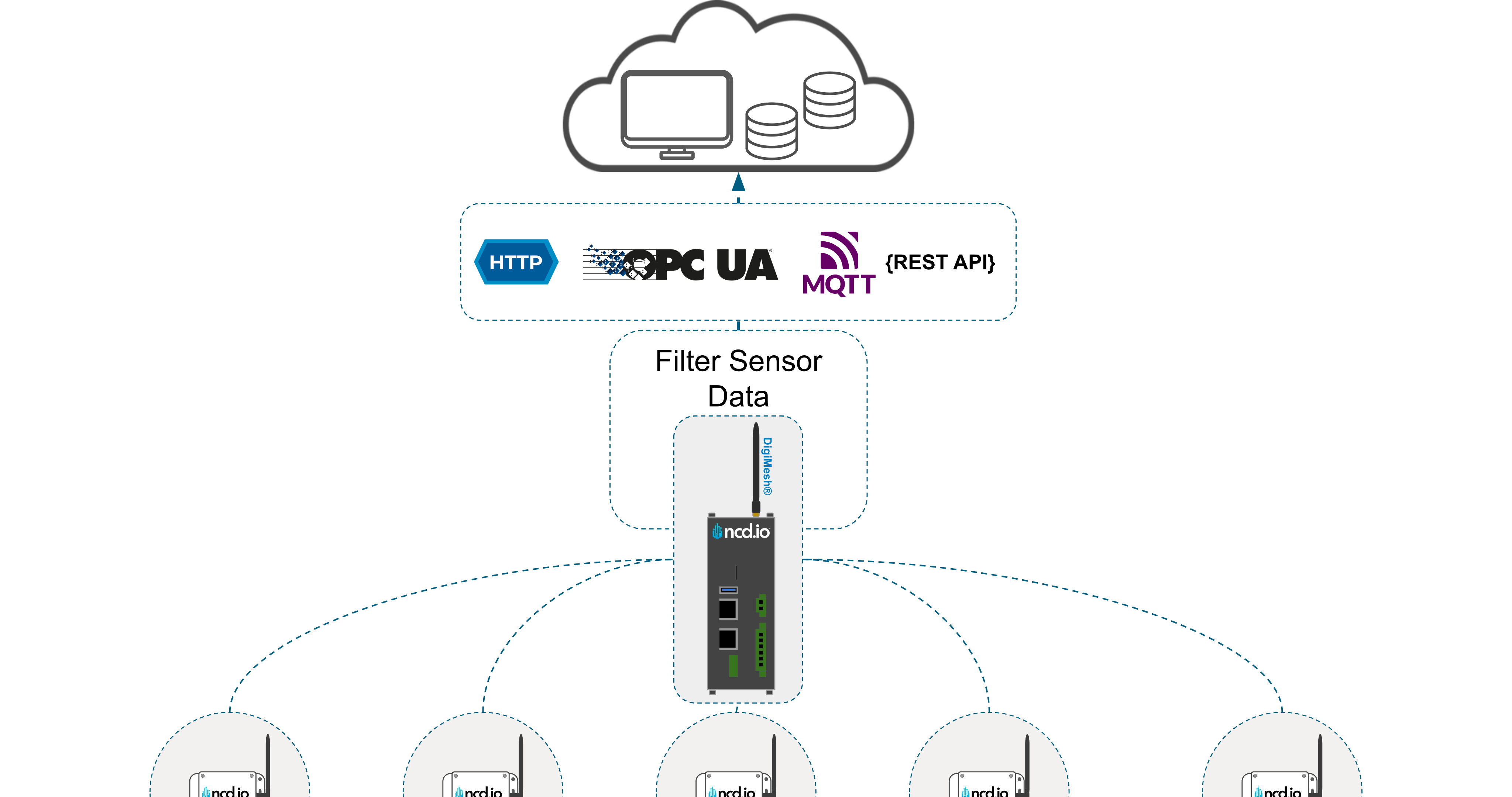
4. Cloud Insights: Cloud AI analyzes long-term trends (e.g., “This bearing fails every 3,000 hours”) and sends optimized parameters back to the Edge gateway.
NCD Enterprise IIoT Gateway
For engineers looking to implement this hybrid architecture without building a custom solution from scratch, the NCD Enterprise IIoT Gateway offers a powerful, industrial-grade platform.
It is designed to bridge low-power wireless NCD sensors (using the robust DigiMesh protocol) with local networks or major cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or custom SCADA systems.
NCD Gateway Versions
NCD offers a tiered product line to match the complexity of your deployment:

- NCD Cloud Gateway: Ideal for pure telemetry applications where data needs to go straight to the cloud via MQTT with minimal local processing.
- NCD Enterprise IIoT Gateway Lite: A cost-effective solution for lighter workloads, perfect for deployments that don’t require cellular connectivity or heavy edge processing.
- NCD Enterprise IIoT Gateway Standard: The flagship rugged device featuring Cellular, WiFi, Ethernet, and full processing power for complex Edge logic.
- NCD Atrium IIoT Gateway (Beta): A complete IoT sensor monitoring and management platform designed specifically for NCD wireless sensors. This enterprise-grade gateway comes fully configured with Node-RED flows, a modern React-based web interface, and over-the-air update capabilities.
Contact us
If you would like to learn more about the features of the NCD Gateway, you can visit the product website or contact our team.
- Cuntact us to talk to a NCD Technicial Support.
- Visit our Blog Entries to learn about emerging trends.
- Shop for solutions from NCD and our partners.
Conclusion
The choice between Edge and Cloud is not binary; it is architectural. By leveraging an Industrial IoT Gateway like the NCD Enterprise series, manufacturers can enjoy the best of both worlds: the immediate responsiveness of the Edge and the analytical power of the Cloud.
Whether you are retrofitting a 50-year-old factory or building a smart facility from the ground up, the gateway is the cornerstone of your digital transformation.
